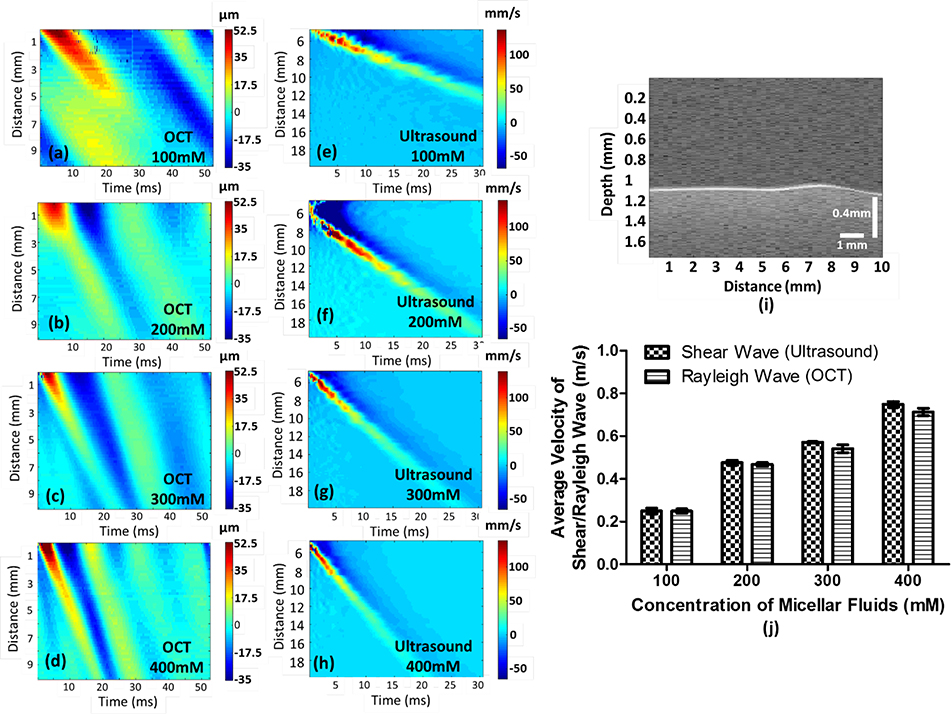
Fig. 2.
Illustration of group velocity measurements in micellar fluids with four concentrations. Figure (a-d) shows the group velocities of Rayleigh waves in micellar fluids measured by ARF in each concentration, as reference dataset, and figure (e-h) demonstrate the group velocities of shear waves generated by the Verasonics ultrasound system. A Rayleigh wave with 300 mM concentration as an example was displayed in figure (i) to express a Rayleigh wave propagating on the surface of a soft matter (see Visualization 1). Ten cases of each concentration have been measured by OCE to obtain the average Rayleigh wave velocity with standard deviation (SD), and five cases have been evaluated by the Verasonics ultrasound system to acquire the average shear-wave velocity with SD as reference dataset, presented in (j). The velocity of Rayleigh waves is approximately 95.5% of the velocity of shear waves.