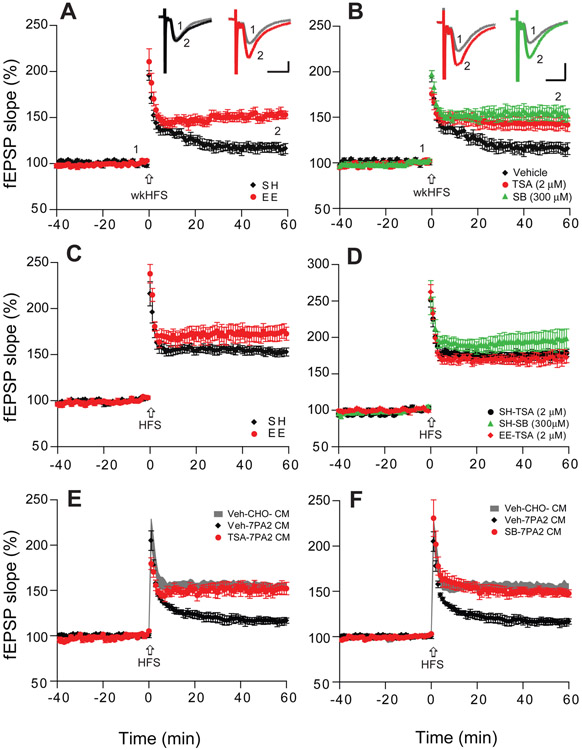
Figure 1. HDAC inhibitors enhance hippocampal LTP and occlude the LTP effect of EE.
(A) A weak high frequency stimulation (wkHFS, arrow) that usually fails to induce a significant hippocampal LTP in CA1 of hippocampal slices of mice kept in standard housing (SH, black, n=8 slices from 6 mice, i.e. n=8/6) can induce a persistent LTP in slices of mice housed in an enriched environment (EE, red, n=9/6). (B) The non-selective HDAC inhibitors, Trichostatin-A (TSA, 2 μM, red, n=8/4) and sodium butyrate (SB, 300 μM, green, n=7/4) enable the weak HFS to induce a significant LTP in slices of SH mice. (C) LTP recorded in CA1 after regular HFS is significantly enhanced in the slices of EE (n=9/6) vs. SH mice (n=9/5). (D) Treating slices with TSA (black, n=8/4) or SB (green, n=9/4) each mimics the EE effect of enhancing LTP in SH mice, and TSA occludes any further enhancement of LTP in EE mice (red). (E) TSA treatment of slices (red, n=8/6) prevents Aβ oligomer-rich 7PA2 CM from impairing LTP. (F) SB treatment of slices likewise prevents 7PA2 CM oligomers from impairing LTP (n=8/6). Inset traces are typical field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) recorded before (gray) and after (black, red or green) HFS for each condition. Horizontal calibration bars: 10 ms; vertical bars: 0.5 mV.