Figure 1.
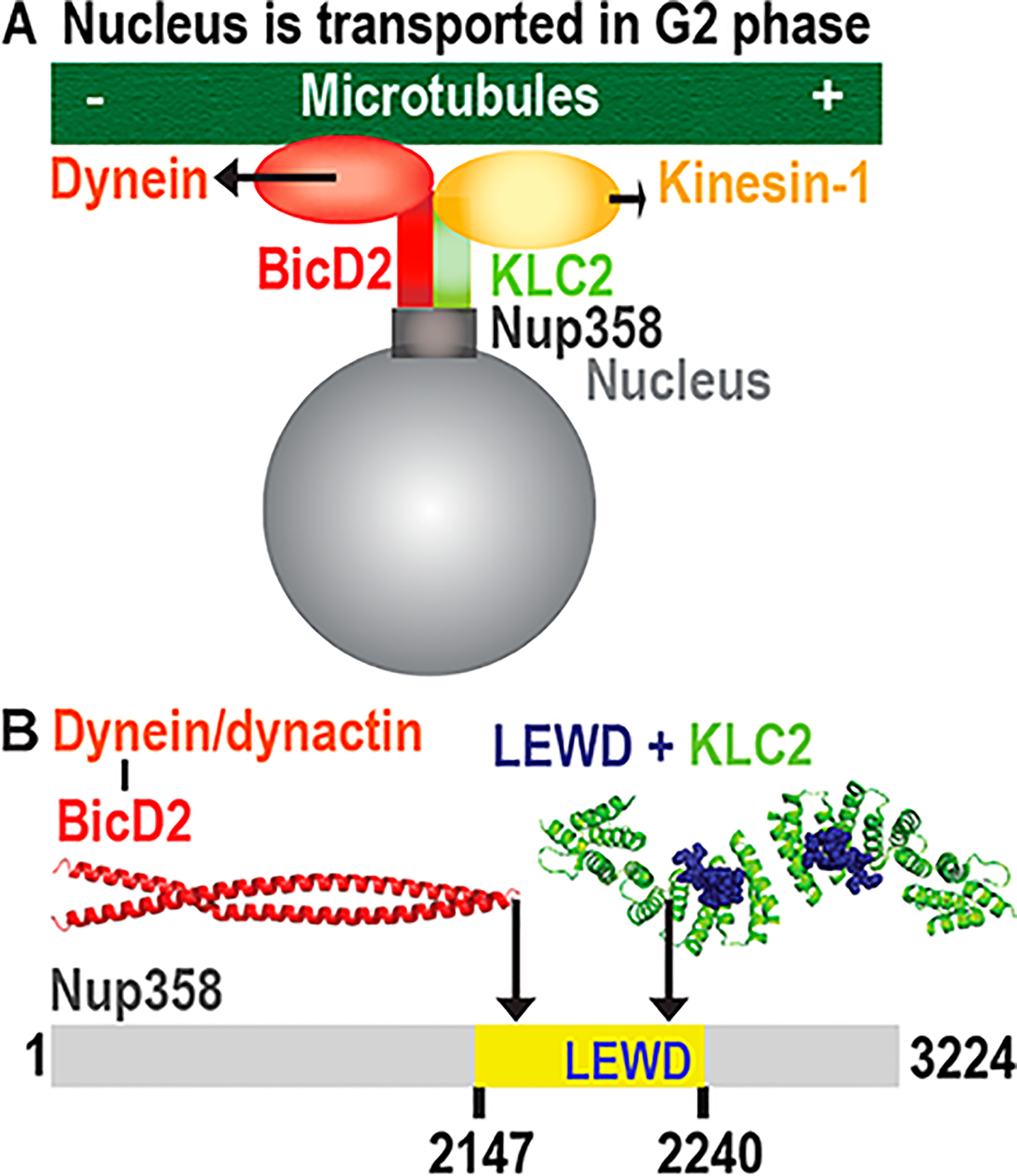
Bidirectional positioning of the nucleus by opposing microtubule motors dynein and kinesin-1. (A) Kinesin-1 and the dynein adaptor BicD2 are recruited to Nup358 during the G2 phase. BicD2 recruits dynein to the nucleus via this pathway.1 (B) Schematic representation of the minimal binding site for BicD2 on Nup358 (yellow). The structure of the cargo/adaptor interacting domain of BicD2 is shown (red).9 This region of BicD2 binds to the cargo adaptor Nup358. A KLC2-binding W-acidic motif (with the sequence LEWD) is located in the mapped minimal BicD2-binding site. The structure of the KLC2-TPR domain that has the W-acidic motif with the sequence LEWD bound is shown.10
