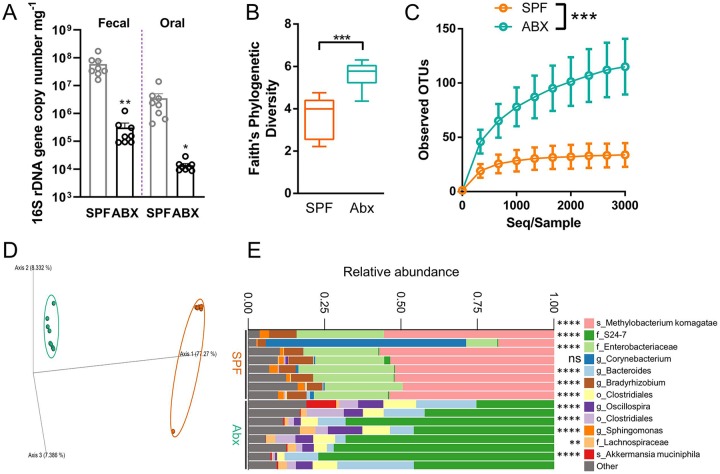
Figure 2.
Broad-spectrum antibiotic (Abx) treatment alters oral microbiota composition in mice. (A) 16S rDNA quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed from genomic DNA extracted from fecal and oral samples collected prior to sacrifice and normalized to the sample weight in milligrams. Significance was calculated with unpaired t tests. The alpha (B, C) and beta (D) diversity of the microbial communities found at the site of ligature placement were calculated by Faith’s phylogenetic diversity, alpha rarefaction plot, and Bray-Curtis dissimilarity principal component analysis, respectively. (E) Microbiota composition is shown at the amplicon sequence variant level. The top 12 variants are classified at the highest taxonomic level identified by sequencing. f_, family; g_, genus; o_, order; s_, species. Significant differences in microbes between specific pathogen–free (SPF) and Abx were calculated with discrete false-discovery rate. Quantified data from panel A are presented as mean ± SEM. Data from panel B are presented as a minimum/maximum box and whisker plot. Data from panel C are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. ****P < 0.0001. ns, not statistically significant.