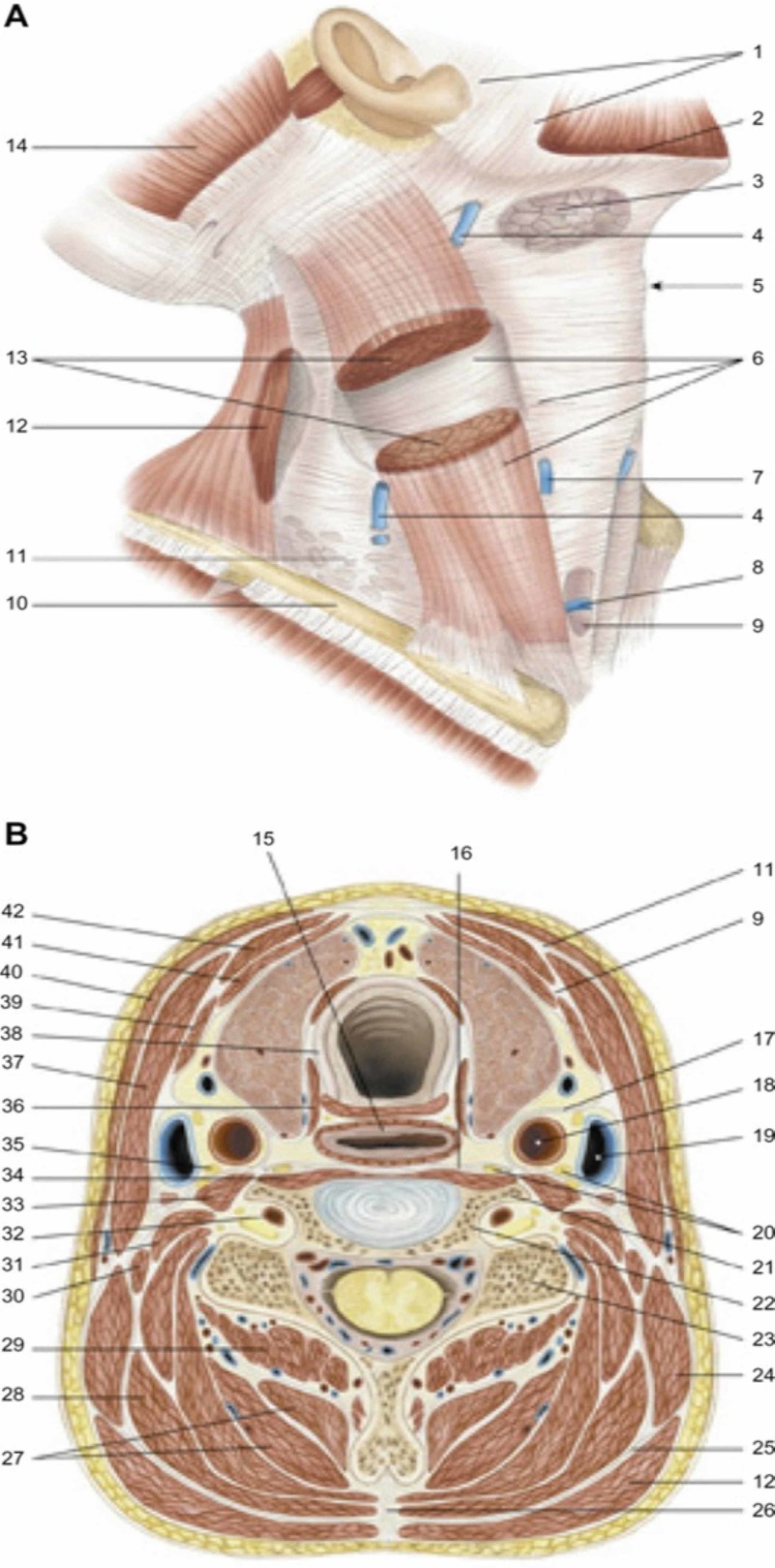
Figure 4. Fascias of the neck.
1: parotid fascia, masseteric fascia; 2: platysma; 3: submandibular gland; 4: external jugular vein; 5: laryngeal prominence; 6: superficial cervical fascia; 7: anterior jugular vein; 8: the jugular venous arch; 9: middle cervical fascia; 10: clavicle; 11: superficial cervical fascia; 12: trapezius muscle; 13: sternocleidomastoid muscle; 14: occipital muscle (of the epicranic muscle); 15: esophagus; 16: deep cervical fascia; 17: carotid sheath; 18: common carotid arter; 19: internal jugular vein; 20: chain of the sympathetic nervous system; 21: 6° cervical vertebrae, anterior tubercle; 22: 6° cervical vertebrae, transverse process; 23: 6° cervical vertebrae, posterior tubercle; 24: levator scapula; 25: nuchal’s fascia; 26: nuchal ligament; 27: semispinalis muscle of the head and neck; 28: splenius muscle of head and neck; 29: multifidus muscle of the neck; 30: posterior scalene muscle; 31: middle scalene muscle; 32: vertebral artery; 33: anterior scalene muscle; 34: long muscle of the neck; 35: phrenic nerve; 36: inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx, cricopharyngeal portion; 37: sternocleidomastoid muscle; 38: trachea; 39: omohyoid muscle; 40: platysma; 41: muscle sternothyroidean; 42: muscle sternohyoidean.
Reproduced with permission Anastasi et al. AA VV, Anatomia dell’uomo, fourth edition, 2010, pp 162. Editor: Edi-Ermes, Milano [Human Anatomy].