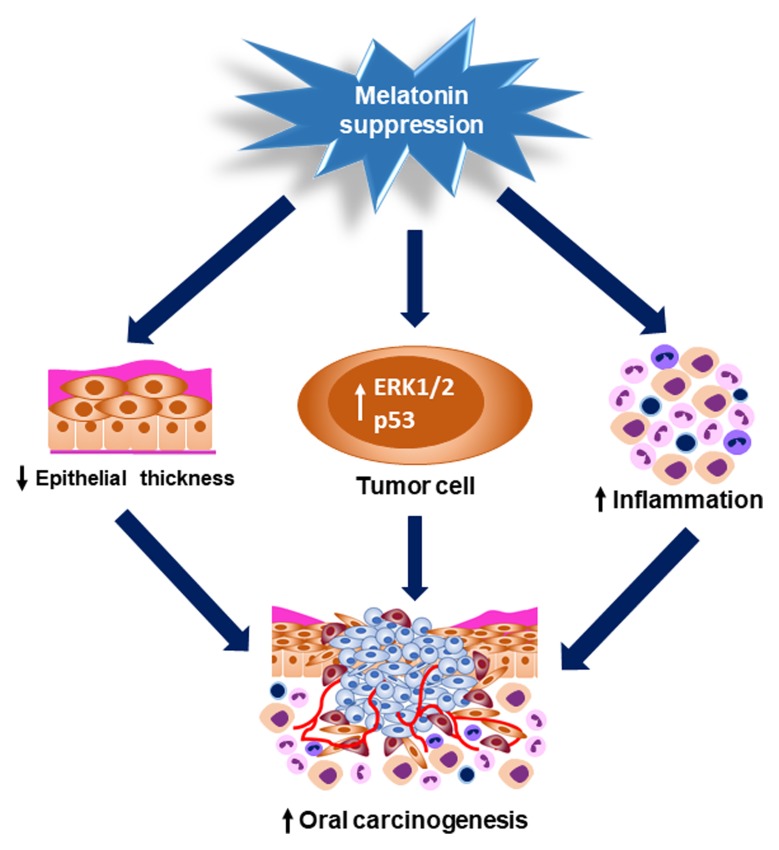
Figure 6. Graphical abstract showing the pinealectomy effects on OSCC occurrence and progression.
Pinealectomy induced a significant reduction of the oral epithelium thickness, which may have increased the mucosa susceptibility to the chemical carcinogen. Moreover, melatonin suppression up-regulated the nuclear levels of ERK1/2 and p53 in the tumor cells and also increased the number of inflammatory cells in the tumor invasive front. All of these mechanisms could contribute to the oral carcinogenesis and tumor progression.