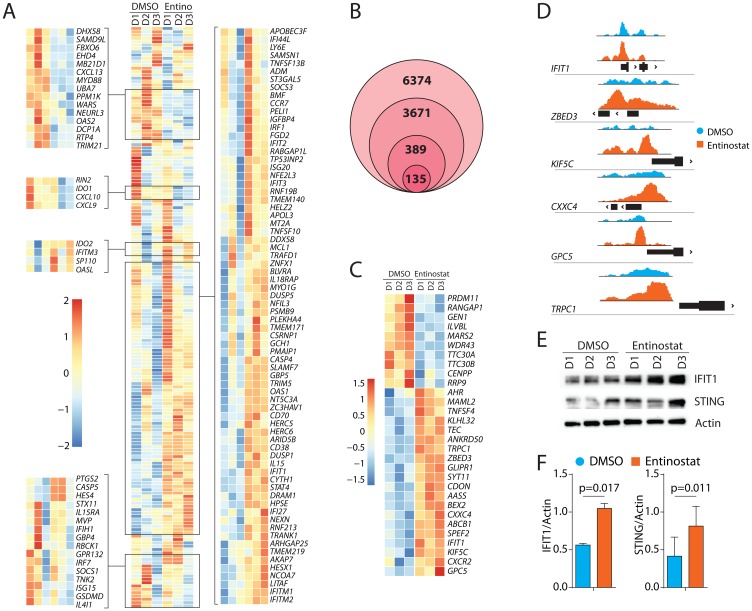
Figure 6. Transcriptomic alterations of IFIT1-associated genes and epigenetic upregulation of IFIT1 by entinostat.
(A) Gene-expression heatmap of genes associated with IFIT1. Heat map showing genes that are altered in human NK cells following entinostat treatment. Differentially expressed gene-set shown was obtained by comparing RNA-Seq of human NK cells treated with or without entinostat with the previously published gene-set obtained from IFIT1 knockdown in THP1 cells [40]. (B) Venn diagram showing filtering of raw (6374) ATAC peaks by protein-coding genes (3671), association with transcription start site (389), and FDR < 0.05 in RNAseq data (135). (C) Gene-expression heatmap of the top 30 genes by log2fold-change identified as areas of increased chromatin accessibility using ATAC-Seq and had an FDR < 0.05 in the RNAseq. (D) ATAC peaks showing the area of increased chromatin accessibility associated with genes with transcriptome log2fold-change greater than two using Integrative Genomics Viewer. Y-axis displays transposase accessibility. Peaks are shown about the genomic location of the promoter region (black box) of the respective gene. (E) Western blot analyses of IFIT1, STING, and β-actin with or without entinostat treatment. One representative western blot is shown out of three independent experiments. (F) Data presented are the mean ± SD three independent western blots. Statistical significance was calculated using a ratio paired t-test from three independent experiments.