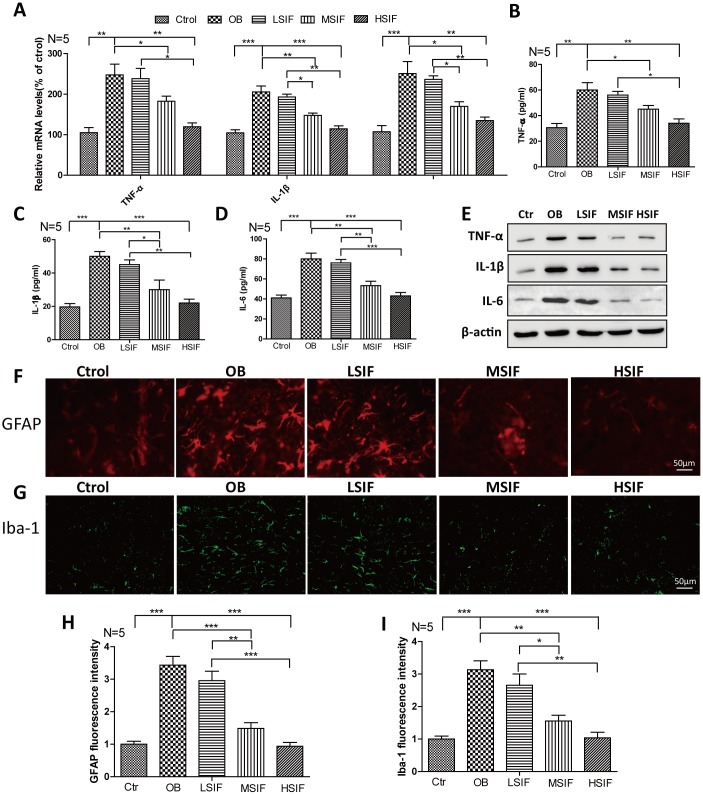
Figure 2.
Soy isoflavones reduce neuroinflammation in hypothalamus of DIO male mice. (A) Quantification shows the mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines in hypothalamus of DIO mice fed with basal diets and the addition with different doses of soy isoflavones; (B–E) Quantification shows the protein levels of inflammatory cytokines in hypothalamus of DIO mice fed with basal diets and the addition with different doses of soy isoflavones by ELISA assay; (F, G) Immunofluorescence staining shows the positive cells of GFAP were reduced in hypothalamus of DIO mice fed with different doses of soy isoflavones compared with the ones fed with basal diets. Scale bar: 50μm. (H, I) Immunofluorescence staining shows the positive cells of Iba-1 were reduced in hypothalamus of DIO mice fed with different doses of soy isoflavones compared with the ones fed with basal diets. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.