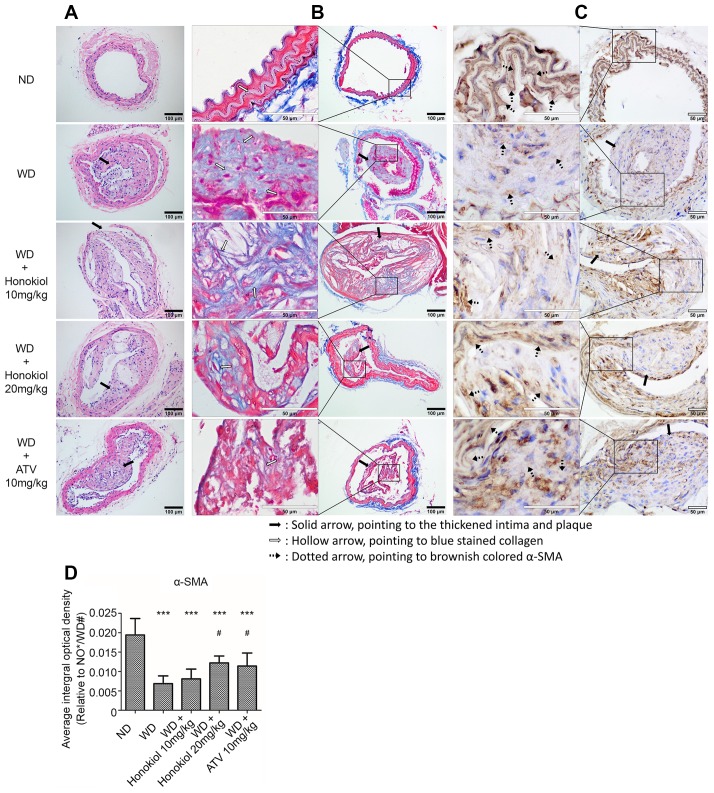
Figure 1.
Effect of honokiol on the formation of carotid atherosclerotic plaque in ApoE-/- mice. (A) Representative HE staining images showing the formation of atherosclerotic plaque and vascular morphology changes (black solid scale bar: 100μm for 200×; black solid arrows point to the thickened intima and plaque). (B) Representative Masson trichrome staining images showing aortic collagen formation (black solid scale bar: 100μm for 200X; hollow scale bar: 50μm for 400X; black solid arrows point to the thickened intima and plaque; hollow arrows point to blue stained collagen). (C) The expression of α-SMA in carotid tissue was assessed by immunohistochemical staining (hollow scale bar: 50μm for 400X; black solid arrows point to the thickened intima and plaque; black dotted arrows point to brownish colored α-SMA). (D) The average integral optical density of α-SMA in carotid tissue was quantitatively analyzed by Gel-Pro Analyzer 4.5 software. (n = 6; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. the ND group. # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001, vs. the WD group; one-way ANOVA). ND: normal diet; WD: Western-type diet; α-SMA: α-smooth muscle actin.