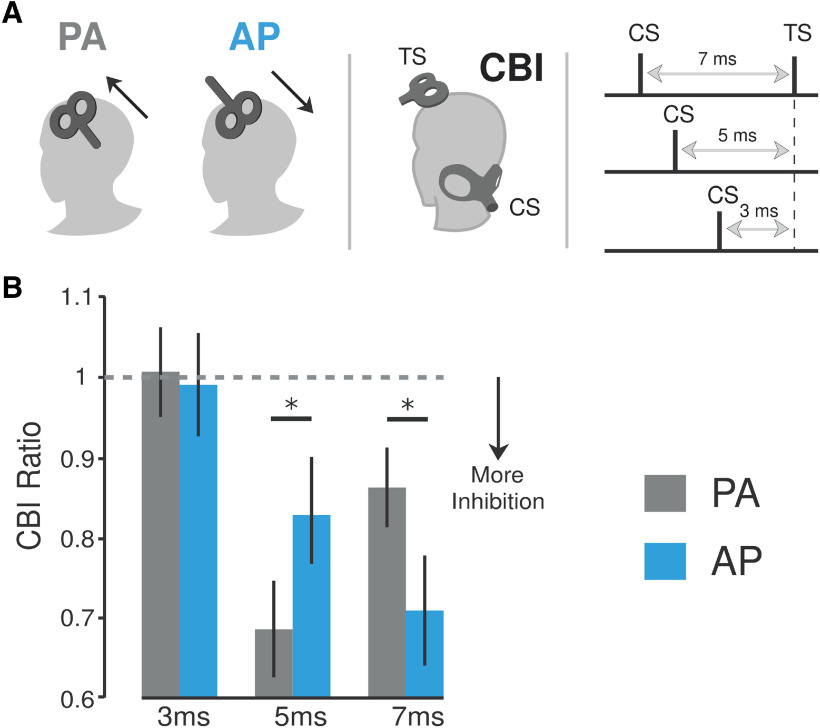
Figure 1.
Effects of different current directions applied over M1 on cerebellar–M1 connectivity (CBI). A, Schematic representation of experiment 1. This experiment tested how applying cerebellar stimulation (i.e., CS) at varying interstimulus intervals before applying a TS to distinct M1 coil orientations (PA vs AP currents) affected CBI. Thus, we tested both PA-CBI and AP-CBI at ISIs of 3, 5, and 7 ms. B, Bar graphs and vertical error bars depict the mean ± SEM (*p ≤ 0.05) of the CBI ratio. The x-axis represents different ISIs (3, 5, and 7 ms) applied for both PA-CBI and AP-CBI. The y-axis shows the CBI as the ratio of the conditioned versus the unconditioned MEP. Ratio values <1 represent inhibition, whereas ratios >1 represent facilitation. CBI values measured with the different M1 currents were matched for test MEP amplitude values ∼1 mV. Here, we found that PA-CBI measured with an ISI of 5 ms elicited stronger CBI than AP-CBI. On the other hand, when measured at 7 ms, AP produced a significantly larger effect than PA-CBI. Importantly, we did not find any evidence of CBI for either M1 current direction when measured at a 3 ms ISI since this interval is presumably too short to elicit any cerebellar effects to cortical regions.