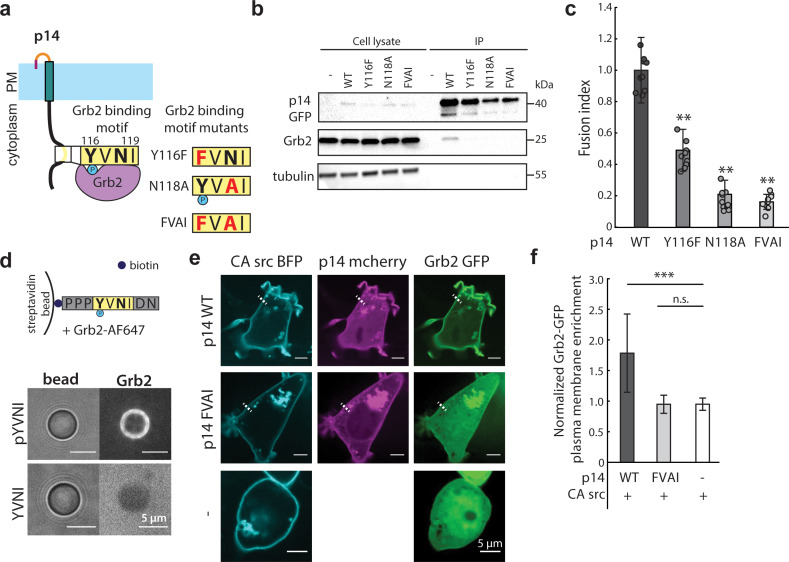
Figure 3. p14 Y116 in the cytoplasmic tail binds to Grb2.
(a) Schematic of p14 mutants that disrupt predicted Grb2 binding motif. (b) Western blot of co-immunoprecipitation of p14 with Grb2 (lane 7) and p14 mutants, Y116F, N118A, FVAI, that does not bind Grb2 (lane 8, 9, 10). (c) Average fusion index of p14 mutants with error bars representing standard deviations from 3 independent transfections of 3 wells each. P-values are two-tailed, two-sample Student’s t-test where *** = p<0.001 (See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1a, (b). (d) Streptavidin beads with biotinylated phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated Y116 p14 cytoplasmic tail peptide encoding (P113-N121) binds and did not bind to purified Grb2 respectively (See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1c, (d). (e) Confocal images of Grb2-GFP (green) enrichment to the plasma membrane of cells co-expressing p14 WT, p14 FVAI mCherry (magenta) and wildtype HEK293T with constitutively active c-src kinase (cyan). (f) Average normalized Grb2-GFP plasma membrane enrichment in cells co-expressing constitutively active c-src and either p14 WT (n = 33 cells) or p14 FVAI (n = 26 cells) or expressing constitively active c-src alone (n = 24 cells). Error bars represent standard deviations from three independent transfsections. P-values are two-tailed, two-sample Student’s t-test where *** = p<0.001 and n.s. = p>0.05.