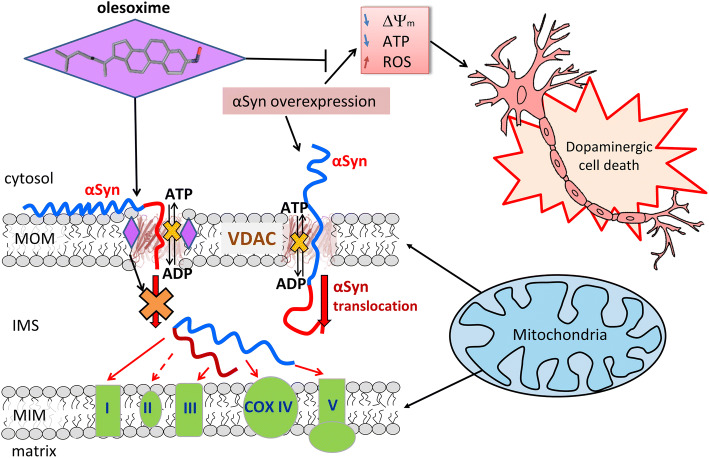
Fig. 6.
Proposed model of olesoxime neuroprotective effect. When αSyn is captured by the VDAC pore it disrupts ATP/ADP fluxes through VDAC. Under normal conditions endogenous αSyn regulates these fluxes by reversibly and dynamically blocking VDAC. Under αSyn overexpression-induced stress αSyn translocates across MOM through VDAC and targets ETC in the MIM causing their impairment, mitochondrial dysfunction and eventually neuronal cell death. Olesoxime partitions into the MOM and hinders αSyn translocation through VDAC by interacting with the pore–lipid interface. This model suggests a tentative mechanism of olesoxime protection of mitochondria integrity and promotion of neuronal cell survival