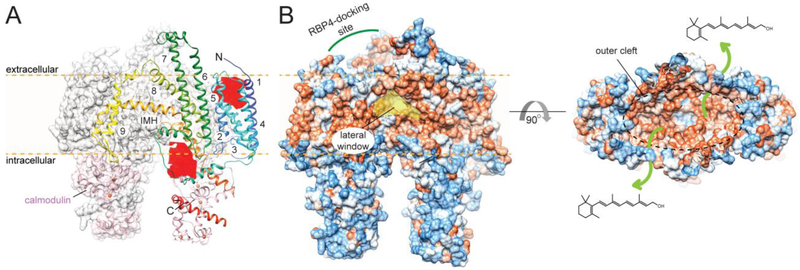
Figure 9– Molecular architecture of STRA6 in complex with calmodulin.
(A) The cryo-EM dimeric structure and lipid membrane topology of the receptor. An individual protomer is shown in color. The numbers indicate transmembrane helices present within the protein. Calmodulin interacting at the intracellular site of STRA6 is shown in pink. Two cavities that represent putative small molecule-binding sites are colored in red. IMH – intramembrane helix. (B) A surface representation of STRA6. Colors from blue to red indicate increasing hydrophobicity. The location of the binding site for holo-RBP4 and a hydrophobic outer cleft as well as the presence of a well-defined lateral window suggest a putative ROL transfer pathway from the binding-protein to the plasma membrane (indicated with green arrows).