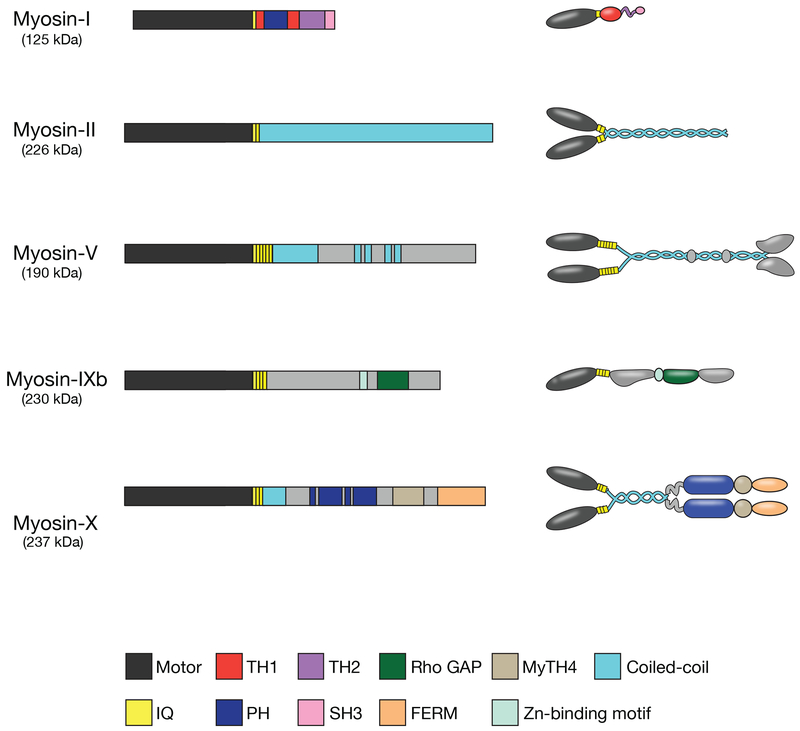
Figure I.
Domain organization and overall structural features of myosin isoforms involved in phagocytosis. Each myosin heavy chain consists of an N-terminal motor domain, a neck domain that binds light chains, and a tail domain that can include coiled-coil motifs to promote dimerization (in myosins-II, -V, and -X), membrane-binding Pleckstrin homology domains (in myosins-I and -X), or protein interaction motifs that promote cargo binding specificity. TH1, tail homology 1; TH2, tail homology 2; PH, Pleckstrin homology; IQ, light chain binding IQ motif; SH3, Src Homology 3; MyTH4, Myosin Tail Homology 4; GAP, GTPase-accelerating protein. Redrawn from [112].