Figure 4. Hif1α Deletion Regulates GZ Exit.
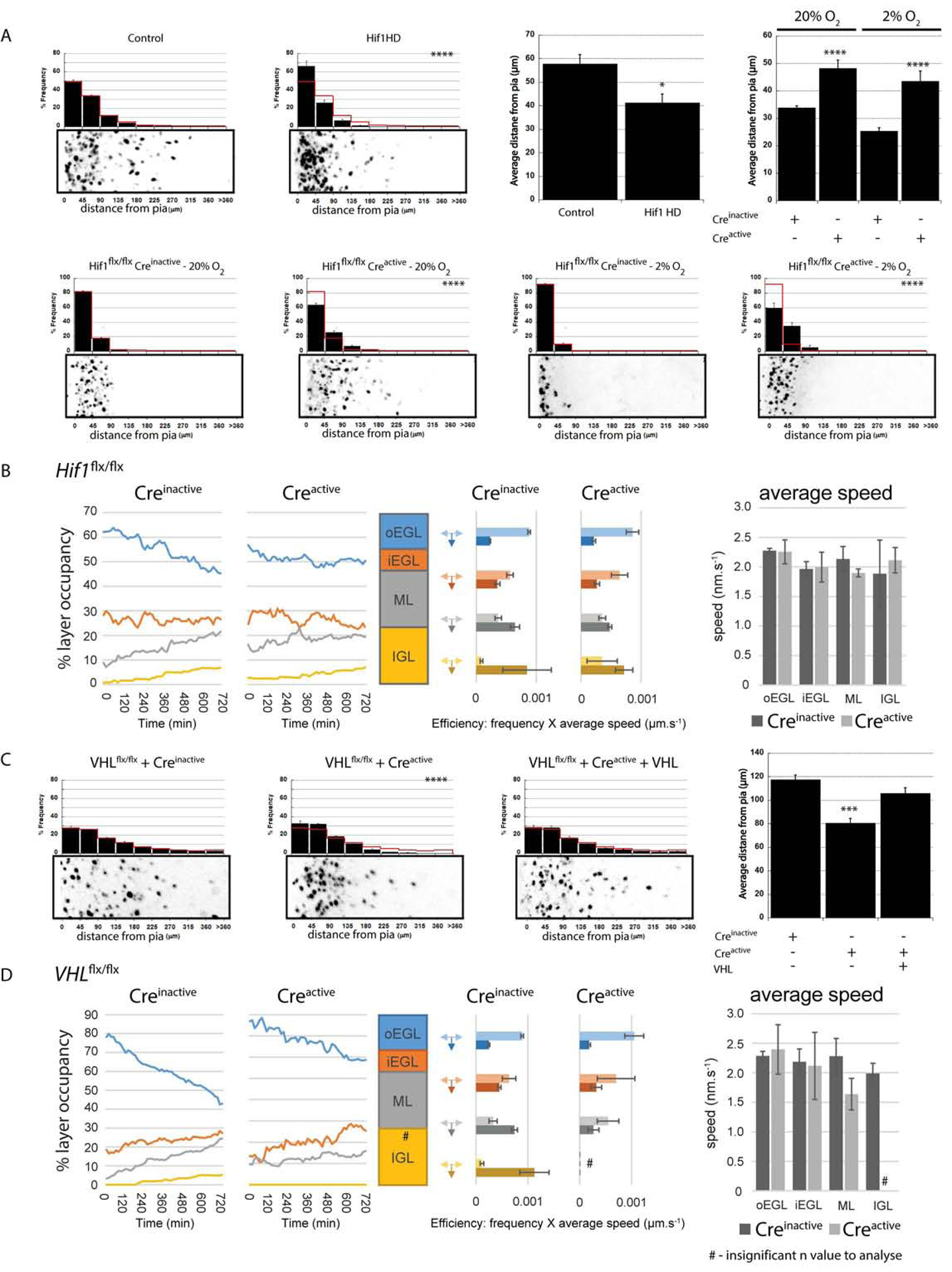
(A) Hydroxylation-deficient Hif1α (Hif1 HD) expression impairs ex vivo CGN migration (41.7±3.6 μm vs. 58.2±4.0 μm in a LacZ controls [χ2 test, P<0.0001, 48h t-test P<0.02]). Expressing Cre recombinase in Hif1αflx/flx cerebella led to precocious migration in 20% O2 (, , P < 0.001) and rescued the 2% O2 migration deficit (, , χ2 and t-test P < 0.0002). (B) Longitudinal time-lapse analysis of ex vivo migration kinetics in Hif1αflx/flx CGNs transfected with Creinactive or Creactive (see Fig. 3B for plot labels). Layer occupancy plots for Hif1αflx/flx CGNs and Hif1α−/− CGNs shows Hif1α−/− CGNs leave the GZ early, but Hif1αflx/flx CGNs quickly catch up (C) Expressing Cre recombinase in VHLflx/flx cerebella reduced ex vivo CGN migration (, , P < 0.0001 [χ2 test] or P < 0.001 [t-test]), but was restored by VHL cDNA (; P < 0.0001 [χ2 test] or P < 0.004 [t-test] vs Creactive). (D) Longitudinal time-lapse analysis of ex vivo migration kinetics in VHLflx/flx CGNs transfected with Creinactive or Creactive (see Fig. 3B for plot labels). Percentage layer occupancy plots show VHL−/− CGNs have delayed GZ exit compared to VHLflx/flx CGNs.
