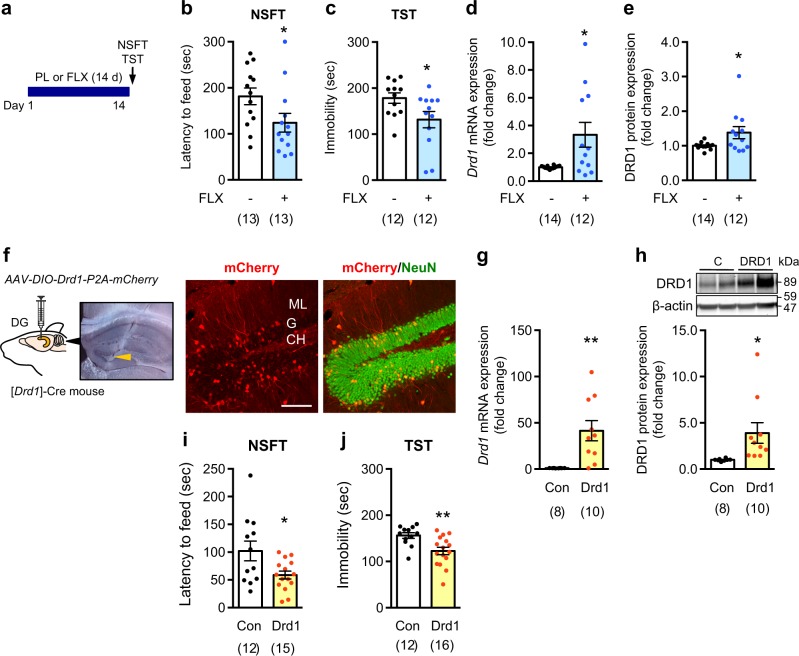
Fig. 4.
Role of D1 receptors on behavioral effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment. a−e Effects of treatment with the placebo (PL) or fluoxetine (FLX; 15 mg/kg/day for 14 days) pellet on the latency to feed in the novelty-suppressed feeding test (NSFT) (b) and the immobility time in the tail suspension test (TST) (c). After the behavioral tests, the expression levels of Drd1 mRNA (d) and protein (e) in the dentate gyrus were evaluated. *p < 0.05 vs. the placebo group; Student’s t test. f−j AAV vectors (AAV-DIO-Drd1-P2A-mCherry or AAV-DIO-YFP) were injected into both sides of the dentate gyrus of [Drd1]-Cre mice to overexpress D1 receptors. An image of the dentate gyrus obtained on the same day of needle insertion showed that the edge of injection needle (arrow head) was in the right place. mCherry was mainly expressed in NeuN-positive granule cells of the dentate gyrus after injection of AAV-DIO-Drd1-P2A-mCherry (f). ML molecular layer, GC granule cell layer, H hilus. Scale bars, 100 µm. Overexpression of D1 receptors in the dentate gyrus was confirmed by measurements of mRNA (g) and protein (h) levels. D1 receptor overexpression in the dentate gyrus decreased the latency to feed in the NSFT (i) and the immobility time in the TST (j). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the control (C) group; Student’s t test. The number of mice is indicated in parentheses under each experimental condition