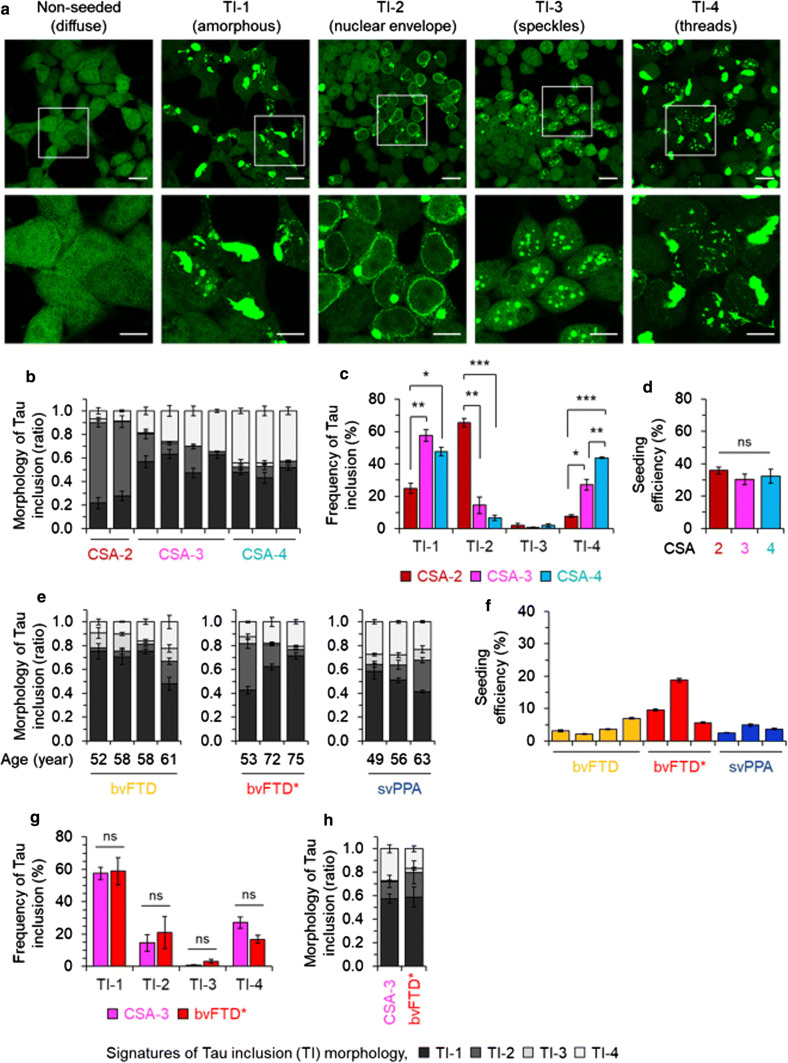
Fig. 6.
Strain-sensitive differential tau seeding assay using YFP reporter cells. a HEK-tauRD-LM-YFP reporter cells express YFP-fused to a human tau repeat domain (RD) with P301L and V337M mutations. In the non-seeded control cells YFP signals are not focal. Cells seeded with tau protein revealed various morphologies of tau inclusions (TIs) characterized by differences in their subcellular distribution; a large mass of aggregated tau (amorphous: TI-1), nuclear envelope and juxtanuclear inclusions (nuclear envelope: TI-2) (reminiscent of “mini-Pick-like bodies'' in granule cells of the dentate gyrus of human cases), granular nuclear inclusions (speckles: TI-3) and thread-shaped inclusions (threads: TI-4) (also seen in human cases). Scale bar, 20 µm and 10 µm in the boxed images. b–d data from mouse brains. Ratio (b) and frequency (c) of TIs observed in HEK-tauRD-LM-YFP reporter cells after seeding with TgTauP301L mouse brains, grouped by Type of CSA signature (types 2, 3 and 4) and normalized by total concentration of tau. Error bars represent SEM. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. ns, not significant. d Relative seeding efficiency of TgTauP301L brains of the different CSA Types analyzed in panels (a–c). Samples were normalized by tau amounts determined by immunoassay. e, f Analyses for human frontal cortex samples (S1 fraction) assigned different diagnoses (Table 1). e Data plotted as per panel (b) also including age at death for individual cases. f Seeding efficiency versus clinical diagnosis; higher efficiencies in bvFTD* samples did not reach significance. g, h Averages of individual mouse brain samples with a CSA Type 3 profile showed similarities to averaged human bvFTD* samples when assessed in pairwise comparisons for inclusion types (g) or plotted by ratios of inclusion morphologies (h)