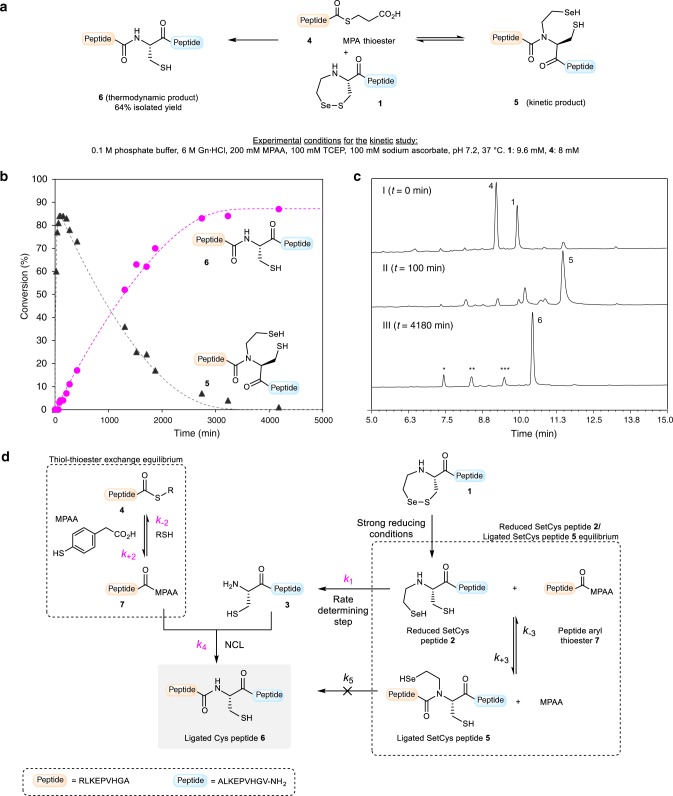
Fig. 4. Insights into the mechanism of SetCys-mediated ligation.
a Ligation of SetCys peptide 1 with peptide thioester 4 in NCL standard conditions yields peptide 6 featuring a native peptide bond to cysteine. b RP-HPLC monitoring of the formation of peptides 5 (black triangles) and 6 (magenta dots) throughout the course of the reaction. Fitting curves for each compound are represented by dashed lines. Each aliquot corresponds to one data point on each trace and was measured once (n = 1). c Representative RP-HPLC chromatograms of the reaction in a at t = 0, 100, and 4180 min (the labeled peaks *, **, *** correspond to TCEP derived-selenophosphine, hydrolysis side-product of peptide thioester 4, and Cys peptide 3, respectively). d Proposed mechanistic model for the ligation of N-(2-selenoethyl)cysteine peptides under strong reducing conditions. The rate constants were obtained by software-assisted numerical integration of rate equations (Kintek explorerTM). Rate constants and associated standard errors were estimated based upon the covariance matrix resulting from nonlinear regression fitting (Supplementary Table 5). Rate constants in magenta were determined separately from model reactions.