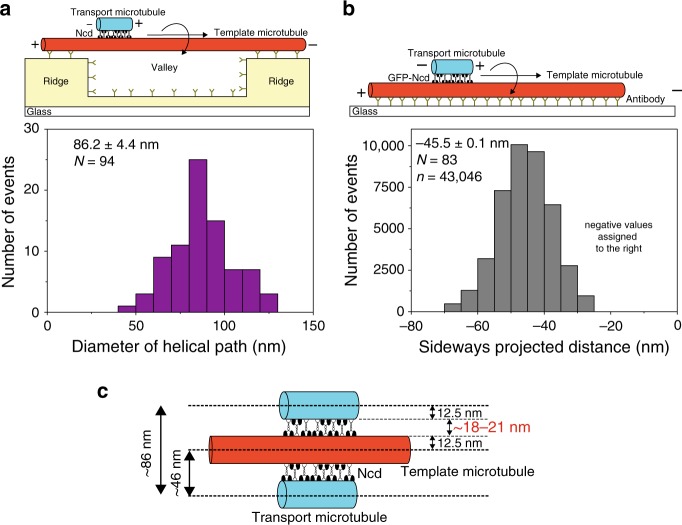
Fig. 3. Spatial extension of Ncd motors between sliding microtubules.
a Histogram corresponding to the diameter of the helical trajectories taken by antiparallel transport microtubules rotating around suspended template microtubules (3D sliding motility assay). The average diameter was 86.2 ± 4.4 nm (N = 94 events; see methods for analysis of distributions with error estimation). The mean diameter of the helical paths was calculated from the peak-to-peak sideways distances obtained from the trajectories of antiparallel transport microtubules. b Histogram corresponding to the sideways distance of antiparallel transport microtubules sliding along the right-hand side of surface-immobilized template microtubule (2D sliding motility assay). The average sideways distance was −45.5 ± 0.1 nm (N = 83 events; n = 43,046 data points). c As shown in the illustration, considering the diameter of the template and transport microtubule (25 nm), the in situ extension of Ncd motors was calculated to be about 18 and 21 nm for the 3D and 2D sliding motility assays, respectively.