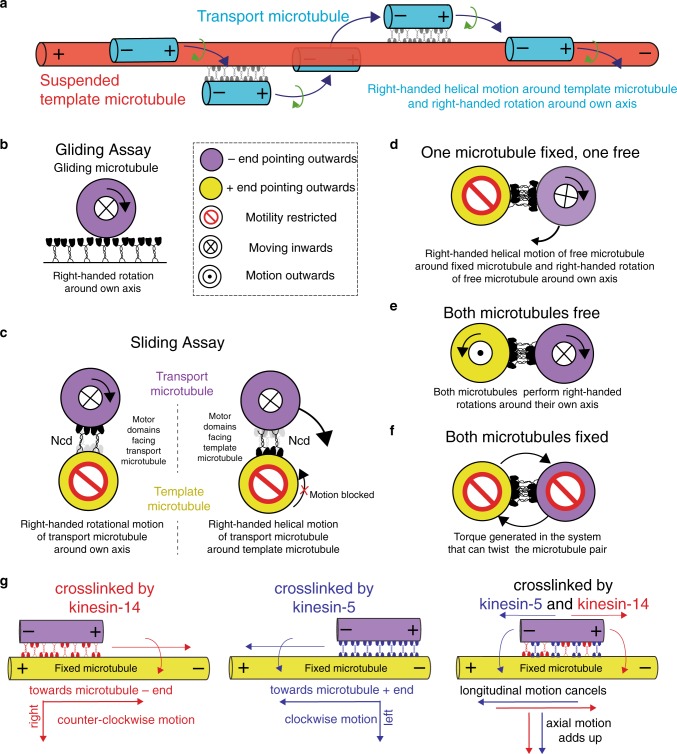
Fig. 6. Illustrations to visualize the motion of antiparallel microtubules cross-linked by Ncd.
a On a suspended template microtubule, antiparallel transport microtubules propelled by Ncd motors exhibit a right-handed helical motion around the template microtubules and a right-handed rotation around their own axis. b, c Transverse sections of microtubules propelled by Ncd in the geometries explored in this work. b In gliding motility assays, microtubules rotate in a right-handed manner while gliding forward. c In sliding motility assays, the Ncd motors bound via their tails to the template microtubule rotate the transport microtubule around its own axis (right-handed), similar to the gliding motility assays. The Ncd motors bound via their tails to the transport microtubule cannot rotate the surface-immobilized template microtubule. This blocked motion is transposed to the transport microtubule, which helically moves around the template microtubule in a right-handed manner. d–f Transverse sections of potential rotational motion and torque generation by microtubules cross-linked by Ncd in vivo. d If one microtubule is fixed and one microtubule is free, the free microtubule will move similar to what is observed for transport microtubules in our sliding motility assays on suspended template microtubules. The free microtubule will exhibit a right-handed helical motion around the template microtubule and a right-handed rotation around its own axis. e If both microtubules are free, they will rotate around their own axis while sliding. f If both microtubules are fixed, they will coil around each other or twist their shape depending on how the microtubules are hinged and how strong the torque generated by the motors is. g While kinesin-14 motors drive the helical motion of transport microtubules towards the minus-end of the template microtubule in a right-handed manner (counter-clockwise motion), kinesin-5 motors drive the helical motion of transport microtubules towards the plus-end of the template microtubule in a left-handed manner (counter-clockwise motion). Therefore, when kinesin-5 and kinesin-14 are acting together in a microtubule overlap, the motion in the longitudinal direction cancels out while the motion in the axial direction adds up.