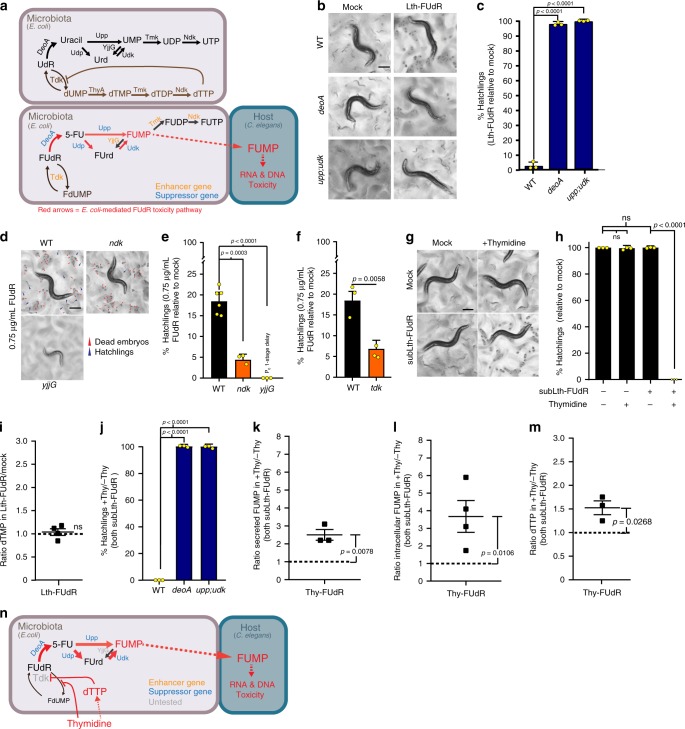
Fig. 1. Dietary thymidine enhances FUdR-to-FUMP conversion in E. coli.
Throughout this figure: % hatchlings is estimated as [live hatchlings/(live hatchlings + live embryos + dead embryos)] in the condition of interest relative to % hatchlings in mock of the same E. coli or C. elegans genotype; ≥5 images per treatment were quantitated; statistical significance was assessed via two-tailed unpaired nonparametric t-test. LC–MS data was analyzed using one-tailed ratio t-test after ROUT outlier treatment. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM, scale bars = 200 µm, n = # independent biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. a Top: endogenous pyrimidine ribonucleotide salvage pathway (black font) and dTMP de novo synthesis pathway (brown font). Bottom: Model of E. coli-mediated FUdR-to-FUMP toxicity pathway. b Representative images of progeny viability of C. elegans treated with mock or Lth-FUdR while cultured on WT (BW25113), deoA, or upp;udk KO E. coli lawns. c Quantification of b treatments. n = 3. d Representative images of progeny viability of C. elegans treated with mock or 0.75 μg/mL FUdR (lower dose to detect enhancers) while cultured on WT (BW25113), ndk, or yjjG KO E. coli lawns. e Quantification of panel d treatments. n = 3. f Quantification of progeny viability of C. elegans treated with mock or 0.75 μg/mL FUdR while cultured on WT (BW25113) or tdk KO E. coli lawns. n = 3. g Representative images of progeny viability of C. elegans treated with FUdR (0.25 μg/mL) ± 5 mg/mL thymidine. h Quantification of g treatments. n = 3. i LC–MS measurement of dTMP normalized to [13C9,15N2]UMP in E. coli treated with Lth-FUdR (5 µg/mL) relative to mock. n = 4. j Quantification of progeny viability of C. elegans cultured on WT (BW25113), upp;udk, or deoA KO E. coli lawns treated with subLth-FUdR (0.25 μg/mL) ± 5 mg/mL thymidine. n = 3. k LC–MS measurement of secreted FUMP in E. coli supernatants normalized to [13C9,15N2]UMP. n = 3. l LC–MS measurement of FUMP normalized to [13C9,15N2]UMP in E. coli pellets, n = 4. m LC–MS measurement of dTTP normalized to [13C9,15N2]UMP in E. coli pellets, n = 3. n Working model of E. coli-mediated thymidine-enhanced FUdR toxicity: (1) thymidine-derived dTTP inhibits Tdk, and (2) dietary thymidine competes with FUdR, thereby promoting FUdR-to-FUMP bioconversion.