Figure 7.
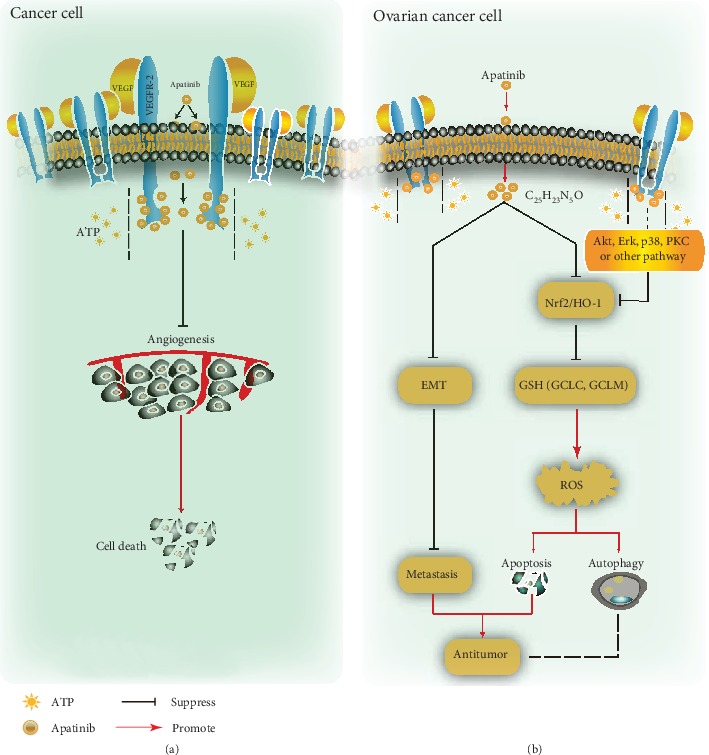
Schematic representation of the antitumor effect of apatinib in cancer cells. (a) After entering the tumor cell, apatinib competes with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for binding to the ATP site of VEGFR2, inhibiting angiogenesis by blocking downstream signal transduction, resulting in tumor cell death. (b) Apatinib inhibits OC cell migration by suppressing EMT and promotes ROS-dependent apoptosis and autophagy through negatively regulating the VEGFR2/Nrf2/HO-1-GSH pathway in OC cells. PKC: protein kinase C.
