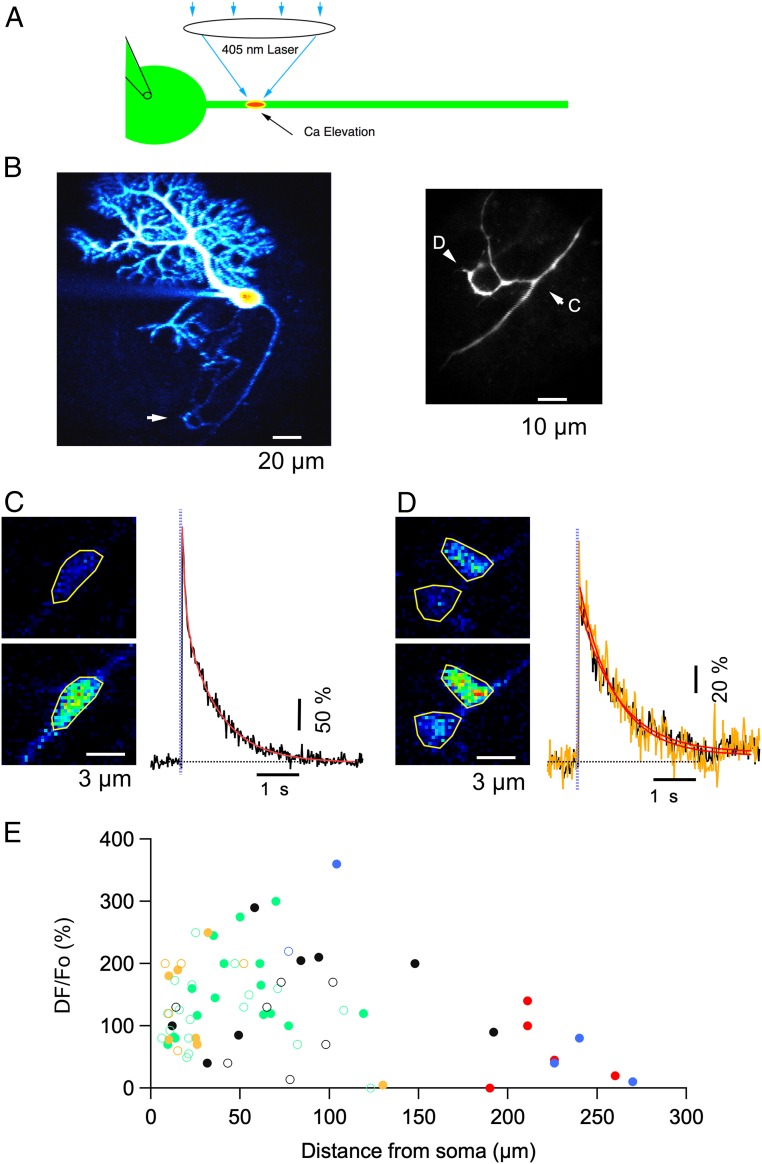
Fig. 2.
Local photolysis reveals functional IP3Rs along PC axons. (A) Schematics of the experimental paradigm: a patch-clamp pipette on the PC soma allows WCR and diffusion into the axon of the Ca probe OG1, of Alexa 594 and of caged IP3. A 405-nm laser beam is directed to specific axonal locations and the ensuing fluorescence changes are monitored with 2PLSM. (B, Left) 2PLSM projection of Alexa 594 fluorescence in a PC with extensive dendritic and axonal arborizations. The expanded view on the Right corresponds to the region highlighted by the white arrow, which includes the first branching point and an axonal collateral that returns to make terminal-like boutons over another PC soma. Labeled arrowheads point to two subregions analyzed in C and D (respectively, a branch point and presynaptic terminals onto a presumptive postsynaptic PC soma). (C, Left) Images from a branch point taken at rest (Upper) and at the peak of the response to a photolysis pulse of 1-ms duration, 1-V amplitude (Bottom). (C, Right) Time course of the ensuing fluorescent rise on the ROI drawn on the peak image. The red trace corresponds to a double exponential fit with time constants and amplitude coefficients of 72 ms, 136% and 0.8 s, 237%. In this and subsequent figures the time of the laser pulse is indicated by purple vertical dots. (D) Similar to C, showing responses in presumptive synaptic terminals. Two ROIs are analyzed in this case (black and yellow traces on the Right), each corresponding to a putative terminal over the PC soma. In these structures, the decay was well approximated by a single exponential with time constants of 0.8 and 0.9 s for the two ROIs, respectively. (E) Pooled data on the peak Cai rises elicited by 2 ms*V (open circles) or 4 ms*V (closed circles) laser pulses at different axonal locations. Values are expressed as ΔF/Fo corresponding to 100*(F-Fo)/(Fo-B) (Methods). The color codes for the morphology are as follows: green for smooth axon, blue for branching points, black for axonal enlargements, red for terminal-like structures, and yellow for axonal stumps.