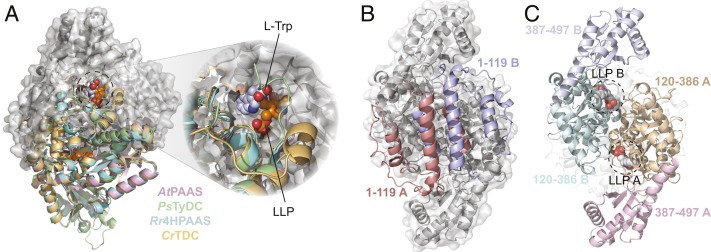
Fig. 2.
The overall structure of plant AAADs. (A) An overlay of the CrTDC (orange), PsTyDC (green), AtPAAS (pink), and Rr4HPAAS (cyan) structures. All four structures exist as highly similar homodimers, but, for visual simplicity, the cartoon structures were only displayed for the bottom monomers. The top monomer of CrTDC is displayed in gray cartoon and surface representation. The dashed circle highlights the CrTDC active site which contains the l-tryptophan substrate and the prosthetic group LLP. (B) The CrTDC N-terminal segments from the two monomers, one colored in salmon and one in blue, form the hydrophobic dimer interface. The remainder of the homodimer is displayed in gray. (C) The configuration of the CrTDC middle (colored in teal and brown) and C-terminal segments (colored in blue and pink) from the two monomers. The N-terminal segments are displayed in transparent gray cartoons, and the prosthetic LLPs are circled and displayed as spheres. The models exhibited in B and C are in the same orientation, which is rotated 90° around the vertical axis from the view in A.