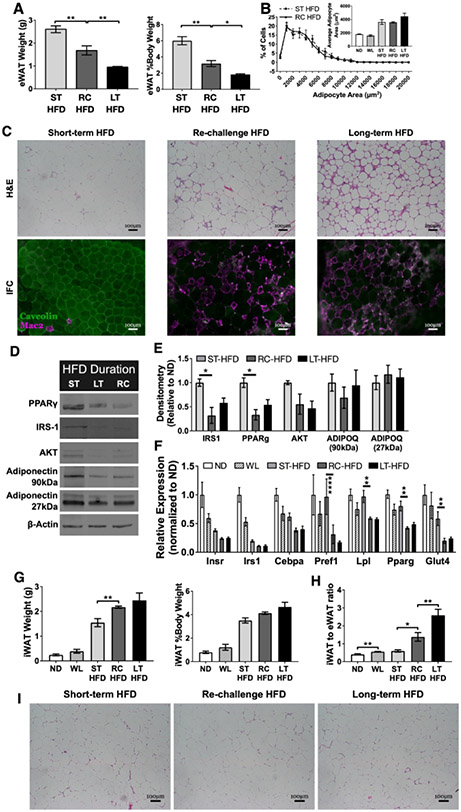
Figure 2 -. HFD re-challenge increases epididymal adipose tissue crown-like structures and reduces expression of proteins essential for mature adipocyte development and function.
(A) Total epididymal WAT (eWAT) weight and as a percent of total body weight (n = 4). (B) eWAT adipocyte size distribution (n = 3 for RC-HFD and n = 4 for other diet conditions). (C) Immunofluorescence and H&E stained eWAT slides representative for each diet condition showing CLS development and maintenance. (D) Representative immunoblots from eWAT showing select adipocyte maturation and insulin signaling proteins. (E) Quantification of densitometry measurements from immunoblots of whole eWAT (n = 3). (F) Expression of adipocyte maturation genes from eWAT (n = 4). (G) Inguinal WAT (iWAT) total weight and as percent of total body weight (n = 4). (H) Ratio of iWAT to eWAT after HFD re-challenge (n = 4). (I) H&E stained iWAT slides representative for each diet condition. Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons for F. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p <0.0001, significance was only compared for ST-HFD versus RC-HFD, LT-HFD versus RC-HFD or ND versus WL.