Figure 3:
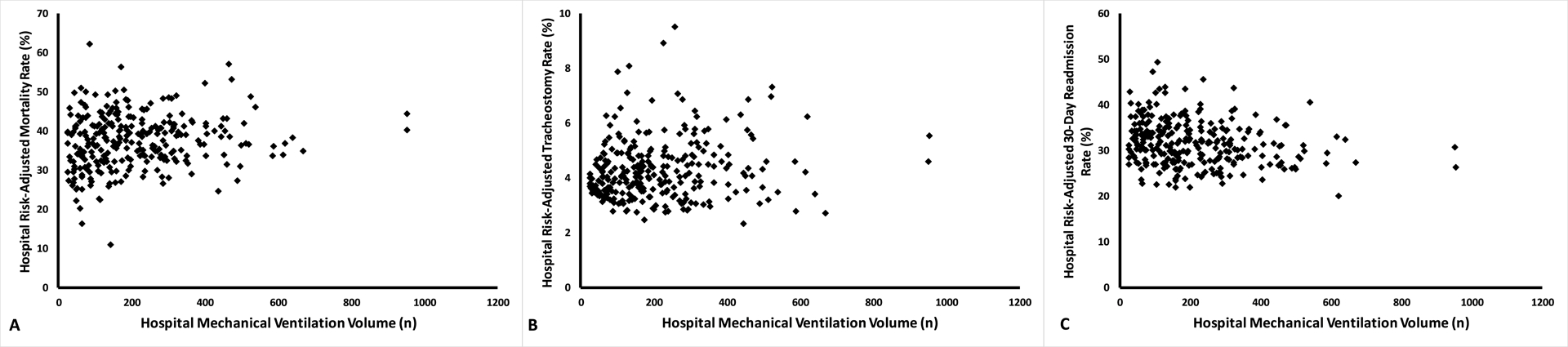
Scatter Plots for Hospital MV Volume and Hospital Risk-Adjusted Outcome Rates Show Weak but Significant Correlation. Hospital risk-adjusted outcome rates were calculated using multivariable hierarchical models with the hospital as a random intercept and Spearman’s correlation test was used to determine nonlinear associations. Higher hospital MV volume was correlated with higher risk-adjusted rates of hospital death (ρ=0.16, p=0.008, Panel A), and tracheostomy (ρ=0.15, p=0.01, Panel B), but lower 30-day readmission (ρ=−0.22, p=0.0002, Panel C). Abbreviations: MV – mechanical ventilation.
