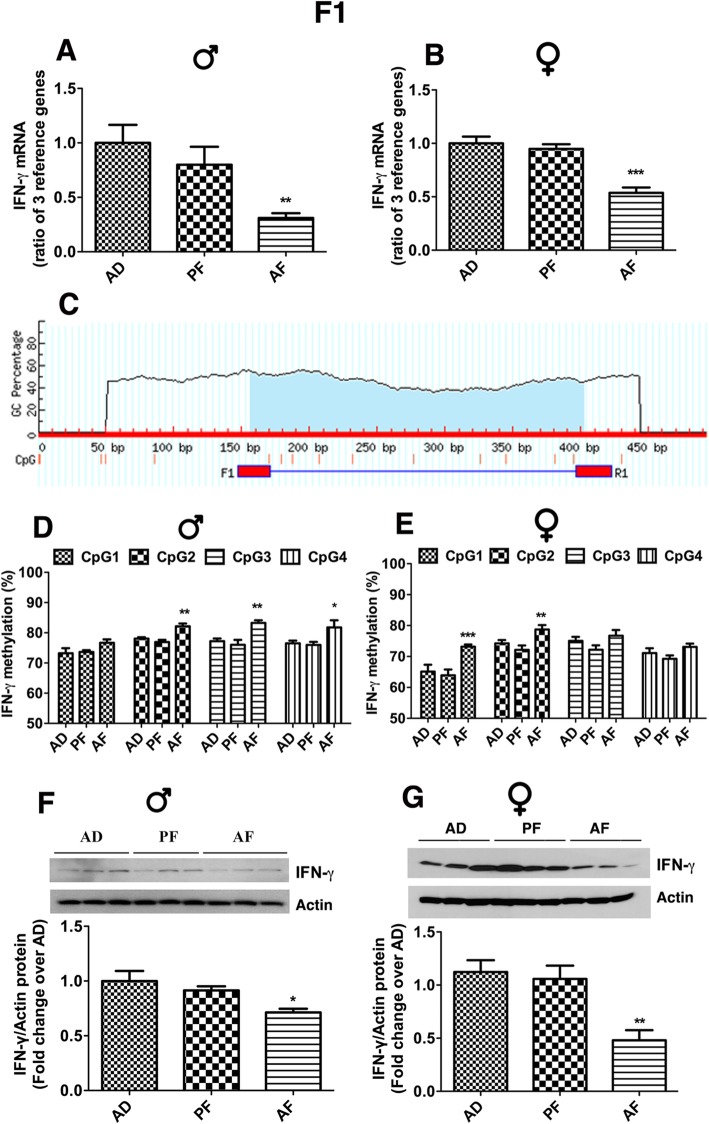
Fig. 1.
Effects of fetal alcohol exposure on Ifn-ɣ gene in the spleen of F1 adult offspring. Changes in the levels of Ifn-ɣ mRNA (a, b), Ifn-ɣ promoter DNA methylation at various CpGs (c–e), and IFN-ɣ protein (f, g) in the spleen of male (♂) and female (♀) fetal alcohol-exposed (AF) and control (AD and PF) rat offspring. a and bIfn-ɣ mRNA levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Data are mean + SEM (n = 8) and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with the Newman-Keuls post-hoc test; ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 between AF and controls. c A schematic diagram of rat IFN-ϒ promoter CpG island identified by the Urogene MethPrimer web tool (http://www.urogene.org/methprimer). d and e. Ifn-ɣ promoter CpG methylation changes were measured by pyrosequencing analysis. Four different CpGs of the IFN-ϒ promoter region—CpG1 (-322), CpG2 (-313), CpG3 (-305), and CpG4 (-285) were analyzed. Data are mean + SEM (n = 8) and were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post-hoc test; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 between AF and controls of the same CpG. f and g IFN-ϒ protein levels in spleen samples were measured by western blotting. Representative blots for IFN-ϒ and β-actin are shown in the upper panel and quantification measurements were represented as a histogram in the lower panel. Data are mean + SEM (n = 6) and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with the Newman-Keuls post-hoc test; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 between AF and controls. F statistics and P values of data shown in figures were presented in Supplementary Table 1