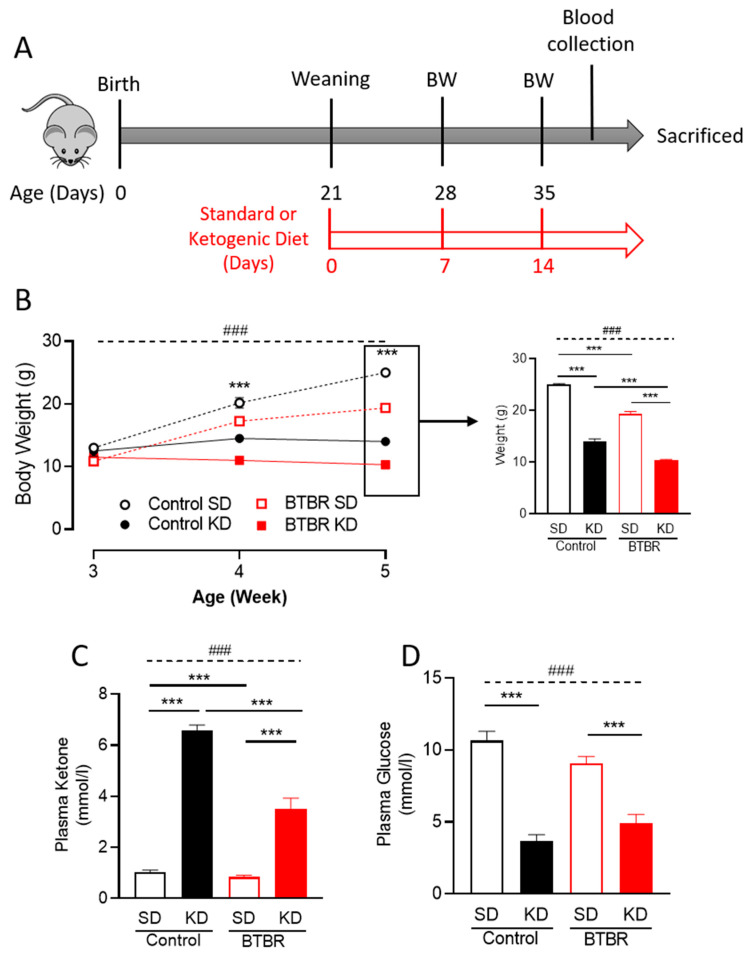
Figure 1.
The ketogenic diet (KD) reduces body weight and induces ketosis in both control and BTBR mice. (A) Schematic drawing of the experimental protocol; after birth of control or BTBR mice, they were kept with their parents with a standard diet. After weaning at postnatal day 21 (PD21), the mice were placed on either a standard or a ketogenic diet. Body weight was measured after 7 and 14 days of diet (PD28 and PD35 weeks of age). Blood was collected to analyze for glucose and circulating ketone bodies. All mice were sacrificed at PD35 (after 2 weeks of diet intervention). (B) Average body weight trajectory of each group in response to the indicated diet (left panel). Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 4–8 per group. Data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. The significant effects (main effects from two-way ANOVA) are presented as: ### p < 0.001. Further, the significant differences between groups in each timepoint revealed by the post-hoc analysis are presented as *** p < 0.001. To explore the body weight changes at PD35 (after two-week diet intervention), single timepoint body weight difference data is presented (right panel). (C) Blood ketone and (D) glucose levels were measured in both control and BTBR mice sacrificed following the two-week diet intervention. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 per group. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. The significant effects (main effects from two-way ANOVA) are presented as ### p < 0.001. Further, the significant differences between groups revealed by the post-hoc analysis are presented as *** p < 0.001. BW: body weight and SD: standard diet.