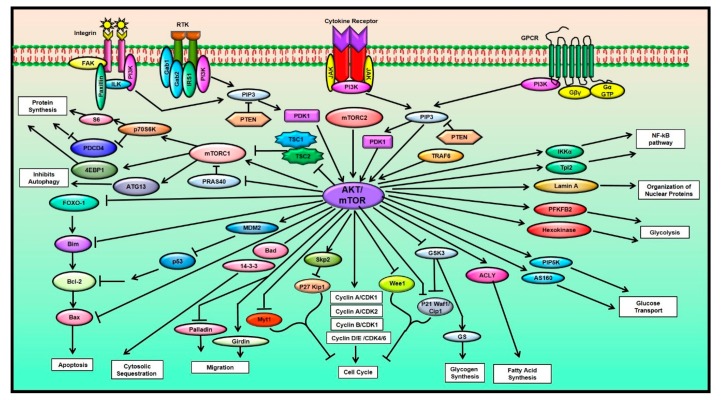
Figure 1.
The AKT/mTOR signaling and its role in various cellular processes (Abbreviations: 4E-BP1: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E)-binding protein 1; ACLY: ATP citrate lyase; AS160: Akt substrate of 160 kDa; ATG13: Autophagy-related protein 13; Bad: Bcl2-associated agonist of cell death; Bax: Bcl 2-associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; CDK: Cyclin-dependent kinase; Cip1: CDK-interacting protein 1; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; FOXO-1: Forkhead box protein O1; Gab1: GRB2-associated-binding protein 1; Gab2: GRB2-associated-binding protein 2; Girdin: Girders of actin filament; GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor; GS: Glycogen synthase; GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase-3; Gα GTP: GTP-bound Gα subunit; Gβγ: G beta-gamma complex; IKKα: IκB Kinase α; ILK: Integrin-linked kinase; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; JAK: Janus kinase; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2 homolog; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; mTORC2: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2; Myt1: Myelin transcription factor 1; P70S6K: 70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase; PDCD4: Programmed cell death protein 4; PDK1: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PFKFB2: 6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2,6-Biphosphatase 2; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol-(3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PIP5K: Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinases; PRA S40: Proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinases; S6: Ribosomal protein S6; Skp2: S-Phase kinase-associated protein 2; Tpl2: Tumor progression locus 2; TRAF6: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; TSC1: Tuberous sclerosis protein 1; TSC2: Tuberous sclerosis protein 2; Wee1: Wee1-like protein kinase).