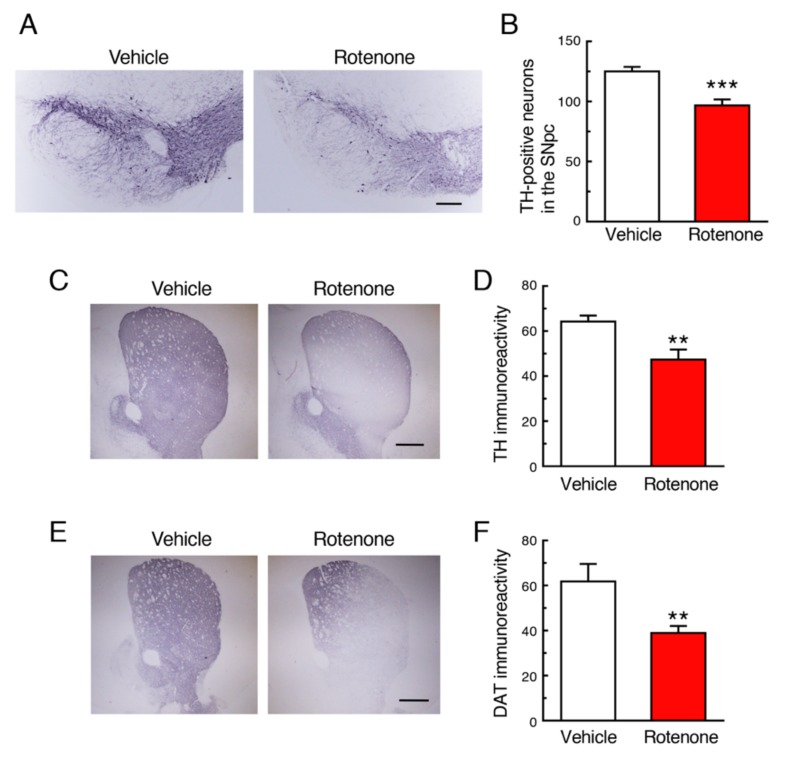
Figure 2.
Chronic exposure to low-dose rotenone induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. (A,C) Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) (A) and striatum (C) of mice 4 weeks after rotenone treatment. Scale bar = 200 µm (A), 500 µm (C). (B) Changes in the number of TH-positive nigral neurons. (D) Changes in the signal intensity of TH immunoreactivity in the striatum. (E) Representative photomicrographs of immunohistochemistry for dopamine transporter (DAT) in the striatum of mice 4 weeks after rotenone treatment. Scale bar = 500 µm. (F) Changes in the signal intensity of DAT immunoreactivity in the striatum. Each value is the mean ± SEM (n = 4). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. the vehicle-treated control group (two-tailed unpaired independent t-test).