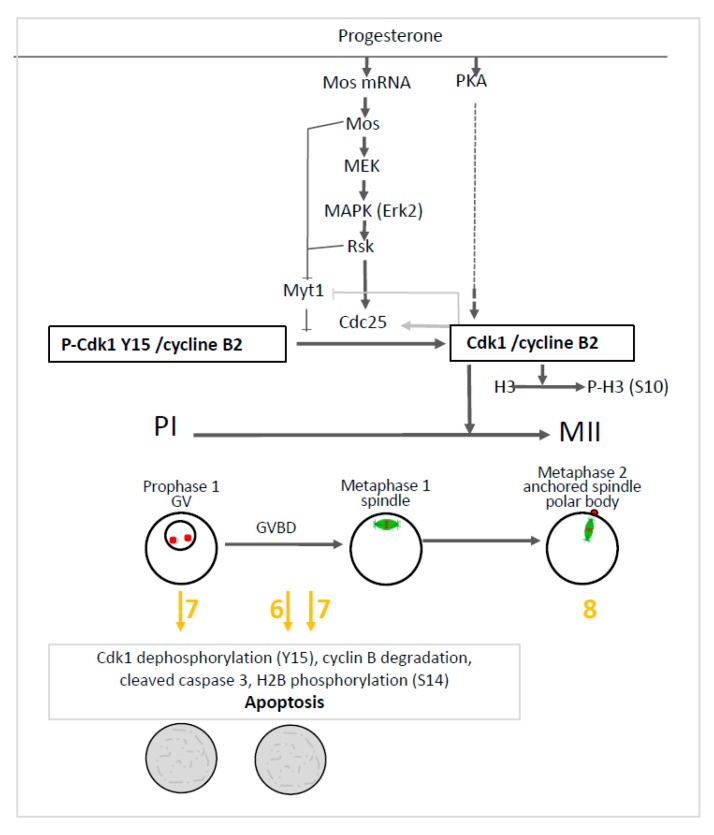
Figure 8.
Effect of ferrocenyl 4-(imino)-1,4-dihydroquinolines on oocytes arrested in prophase I (PI) and oocytes induced to progress in metaphase II (MII). Progesterone activates PKA, Mos synthesis and the MAPKK/MAPK/Rsk cascade. The two pathways further activate phosphatase Cdc25, inhibit kinase Myt1 and converge to activate the Cdk1/cyclin B complex. Rsk, Mos and the activated Cdk1/cyclin B complex inhibit Myt1. The activated Cdk1/cyclin B complex also activates Cdc25 and phosphorylates histone H3. The germinal vesicle (GV) of prophase I oocytes is disrupted (GVBD) upon progesterone addition and the oocytes progress into metaphase I and metaphase II. The nuclear spindle (microtubules-green and chromosomes-red) is formed in metaphase I, is attached to the plasma membrane in metaphase II and accompanied by the emission of a polar body. Ferrocenyl 4-(imino)-1,4-dihydroquinolines 6, 7 (in yellow/orange) induce Cdk1 dephosphorylation, cyclin B degradation, caspase 3 cleavage and histone H2B phosphorylation leading to oocytes apoptosis after meiosis resumption has been triggered by progesterone addition (grey rectangle). Compound 7 produces the same effect on prophase I arrested oocytes. Compound 8 (in yellow/orange) did not affect oocyte progression into metaphase II.