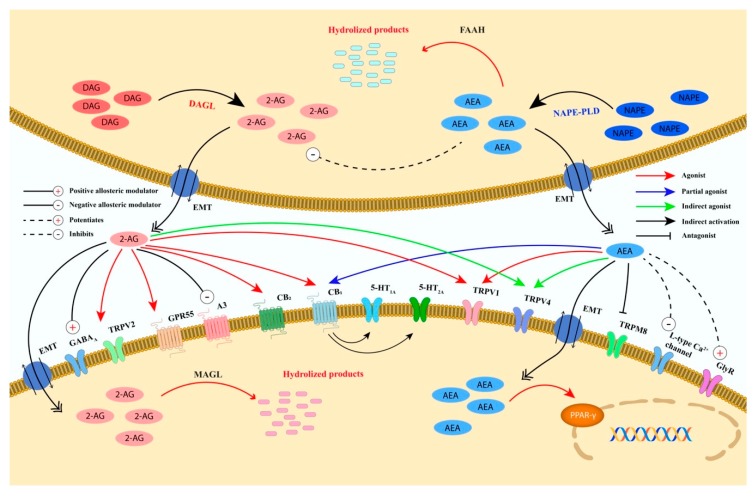
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the biosynthesis, degradation, and receptors’ binding of AEA and 2-AG. Anandamide and 2-AG are postsynaptically biosynthesized from the membrane’s phospholipids and degraded with different pathways and enzymes. AEA is mainly synthesized from NAPE by NAPE-PLD, whereas 2-AG is biosynthesized from DAG by DAGL-α and DAGL-β. The degradation of AEA is catalyzed by FAAH that is mainly expressed postsynaptically. 2-AG is degraded by MAGL that is expressed presynaptically and by two hydrolases named ABHD6 and ABHD12, expressed postsynaptically. Furthermore, AEA and 2-AG catabolism might also occur by the activity of other enzymes (e.g., NAAA, COX-2, and several LOX isoenzymes). AEA and 2-AG retrogradely activate presynaptic CB1. AEA is almost inactive on CB2, whereas 2-AG acts as a full agonist. In addition, AEA, directly or indirectly, also modulates the receptors/channels CB1, CB2, TRPV1 (at postsynaptic and presynaptic level), TRPV4, TRPM8, PPARγ, 5-HT1A, 5HT2A, L-type Ca2+channel, GlyR and negatively regulates 2-AG biosynthesis. 2-AG, directly or indirectly, modulates the receptors/channels TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV4, GPR55, A3 adenosine, GABAA, 5-HT1A, and 5HT2A. The activation of CB1 by 2-AG suppresses either GABA or glutamate release. Abbreviations: ABDH6/12, αβ-hydrolase domain 6/12; AEA, anandamide; 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; CB1, cannabinoid receptor 1; CB2, cannabinoid receptor 2; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; DAG, diacylglycerol; DAGL-α and DAGL-β, diacylglycerol lipase-α and β isoforms; EMT, endocannabinoid membrane transporter; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GABAA, γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor; GlyR, glycine receptor; GPR55, G protein-coupled receptor 55; 5-HT1A, 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor; 5-HT2A, 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor; LOX, lipoxygenase; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; NAAA, N-acylethanolamine hydrolyzing acid amidase; NAPE-PLD, N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor type-γ; TRPM8, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 8; TRPV2, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 2; TRPV4, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 channel.