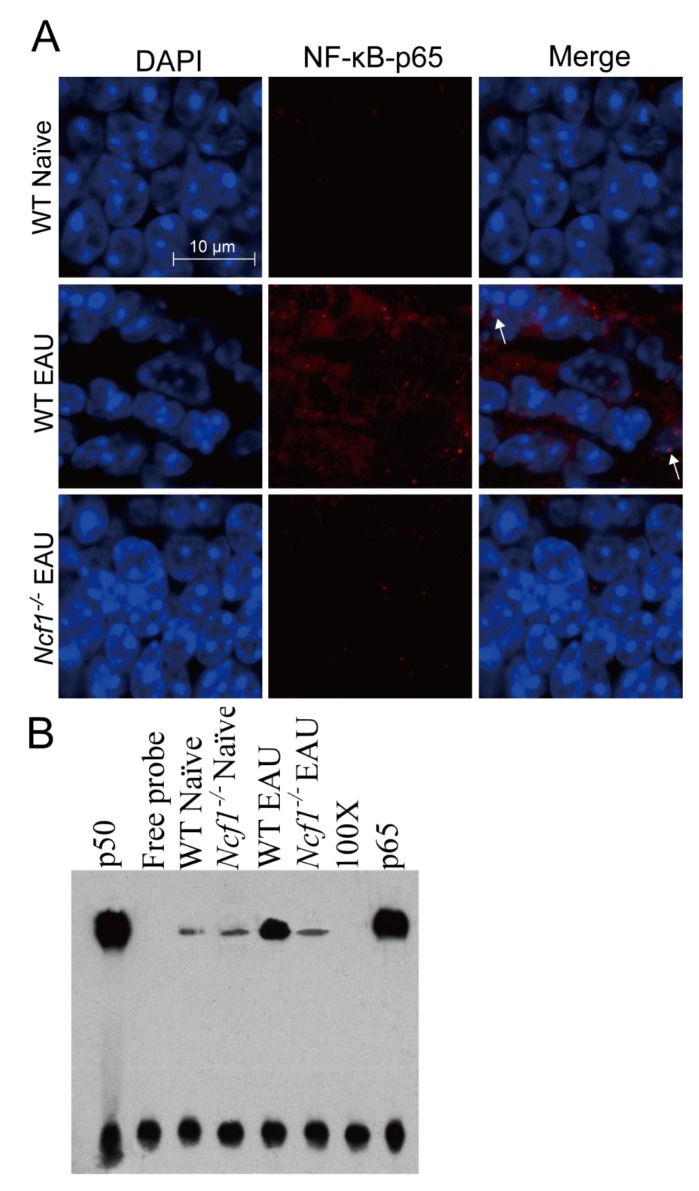
Figure 4.
Absence of Ncf1 reduces NF-κB activation in the retinas of mice with EAU induction. Eyes and retinas of wild-type (WT) and Ncf1−/− mice without (naïve) or with EAU induction were subjected to immunofluorescence staining with DAPI for nuclei and with antibody for NF-κB (p65) (A) and to electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) (B). In panel A, the outer nuclear layer of the retina is shown. Images are representative of at least four samples per group from two independent experiments. Arrows indicate NF-κB in the nucleus. In panel B, lane 1: p50 subunit of NF-κB; lane 2: free probe; lane 3: wild-type naïve mice; lane 4: Ncf1−/− naïve mice; lane 5: wild-type EAU mice; lane 6: Ncf1−/− EAU mice; lane 7: 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled NF-κB probe. Lane 8: biotinylated probe with anti-p65 antibody. Top bands are the complexes of p50/p65/biotin-labeled DNA probe and bottom bands are free probe.