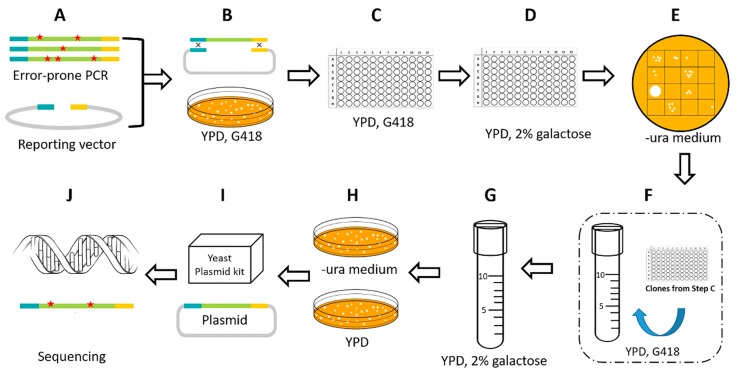
Figure 2.
High-throughput screening process. (A,B) Generation of a mutant library of piggyBac transposase by error-prone PCR and a gap-repair system in yeast. (C–E) The first qualitative screening step. The mutants were grown and induced in a 96-well plates. After 24 h of galactose induction, the solution was diluted and spotted onto the uracil-deficient medium. Mutants that could reverse more clones were chosen for further quantitative analysis. (F–H) The second quantitative screening step. The mutants that were chosen from E and isolated from the C were grown and induced in 12 mL tubes. The concentration was adjusted to ensure a consistent growth condition. After 24 h of galactose induction, the solution was diluted and spread on the -ura medium plate and the YPD plate as control. The transposition efficiency was calculated and compared to the non-mutation one. (I) The isolated clones that exhibited high transpose activity were picked out and the plasmids were extracted. (J) The transposase fragment was sequenced for mutation site analysis.