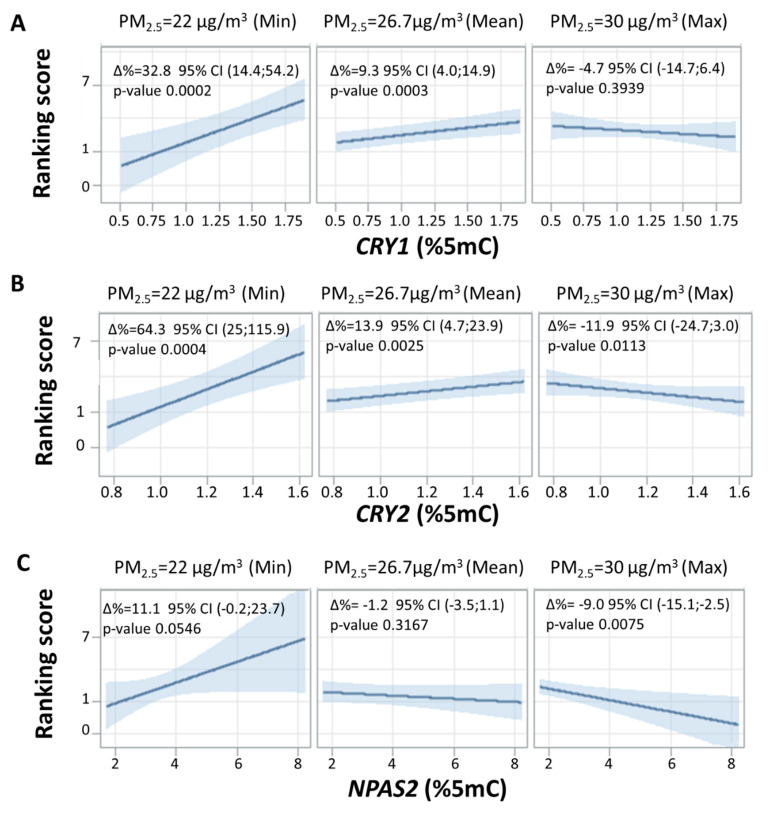
Figure 3.
Interaction effect of PM2.5 annual average and clock gene methylation on Modified Rankin Scale for Neurological Disability. Strength of association between clock gene methylation and Rankin score on natural logarithmic scale at three selected levels of annual average PM2.5 (min, mean, and max). Panels (A–C) represent CRY1, CRY2, and NPAS2, respectively. For all panels, ∆% is equal to (exp(β/10)–1) × 100 and represents the percentage increase in Rankin score for 0.15mC% increment in CRY1/CRY2/NPAS2 methylation at each concentration of annual average PM2.5. Linear regression models were adjusted for age, sex, smoking habits, therapy, diabetes, hypertension, plate, and warm/cold months (months with heaters switched on/off).