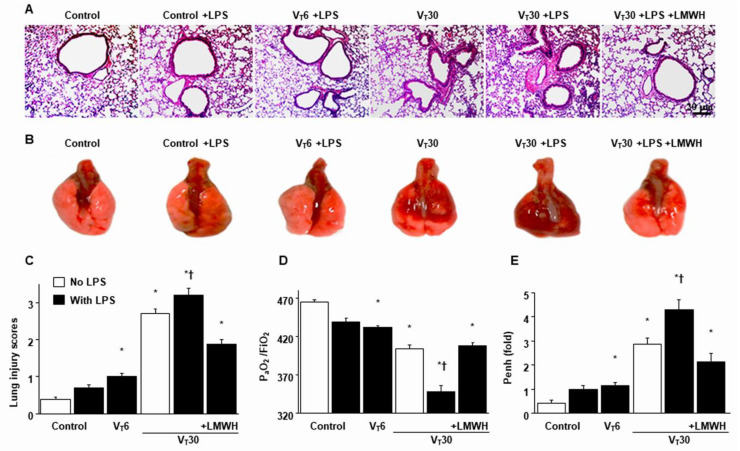
Figure 1.
Suppression of endotoxin-augmented lung stretch-induced lung damage, hypoxemia and impaired respiratory function by enoxaparin (A) Histological examination (100×), (B) gross pathologic findings, (C) lung injury scores, (D) PaO2/FiO2 and (E) enhanced pause from the same animals were from the lungs of nonventilated control mice and those subjected to a tidal volume of 6 mL/kg (VT 6) or 30 mL/kg (VT 30) for 5 h with or without LPS administration (n = 5 per group). Enoxaparin, 4 mg/kg, was given subcutaneously 30 min before mechanical ventilation. Scale bars represent 20 μm. * p < 0.05 versus the nonventilated control mice with LPS; † p < 0.05 versus all other groups. FiO2 = fraction of inspired oxygen; LPS = lipopolysaccharide; LMWH = low-molecular-weight heparin; PaO2 = partial pressure of oxygen; Penh = enhanced pause.