Figure 1.
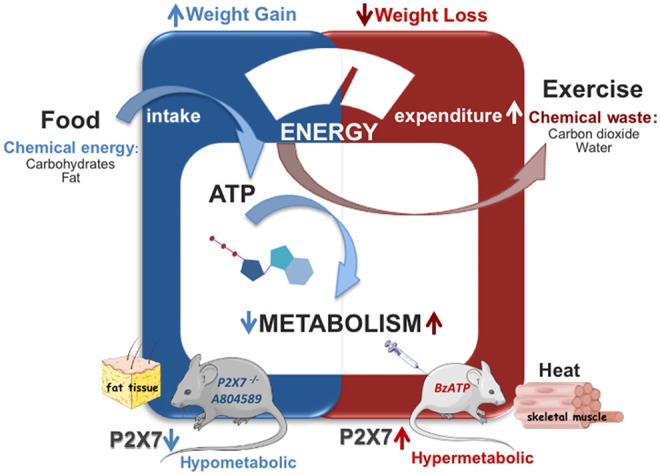
Role of P2X7 in energy metabolism. Genetic deletion or subchronic pharamacological inhibition of P2X7 (A804589) decreases the whole body energy expenditure causing weight gain without affecting food intake (in blue). Stimulation of P2X7 by BzATP enhances energy expenditure and fatty acid oxidation causing weight loss and heat production in mice (in red).
