Figure 1.
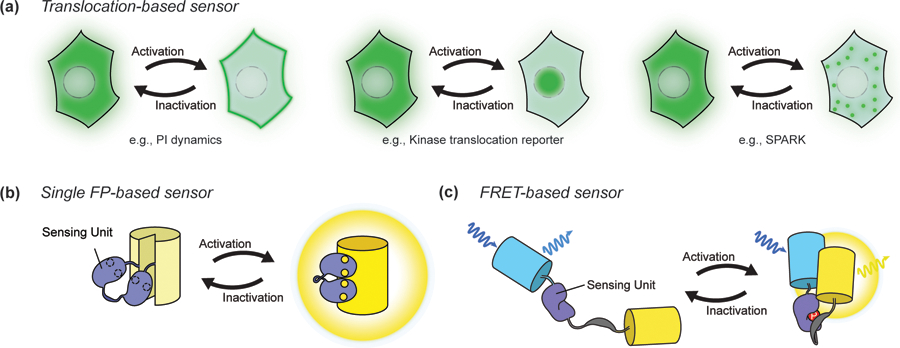
Basic biosensor designs. A. Translocation-based biosensors. Phosphoinositide (PI) sensors utilize lipid-selective binding domains that translocate to or from the membrane to report the production and degradation of specific PIs, such as PIP3 (a). Kinase translocation reporters similarly undergo translocation into or out of the nucleus depending on the phosphorylation of kinase-specific substrate sequences within the reporter (b). SPARK, a phase separation-based kinase reporter, visualizes dynamics of kinase activity with phase separation (c). B. Single FP-based sensor. The insertion of a conformational switch into a single FP can be used to alter chromophore behavior in response to a signaling event. C. FRET-based sensor. Changes in the proximity or orientation between a pair of FPs caused by the sensing unit upon detection of a signaling event results in a change in FRET.
