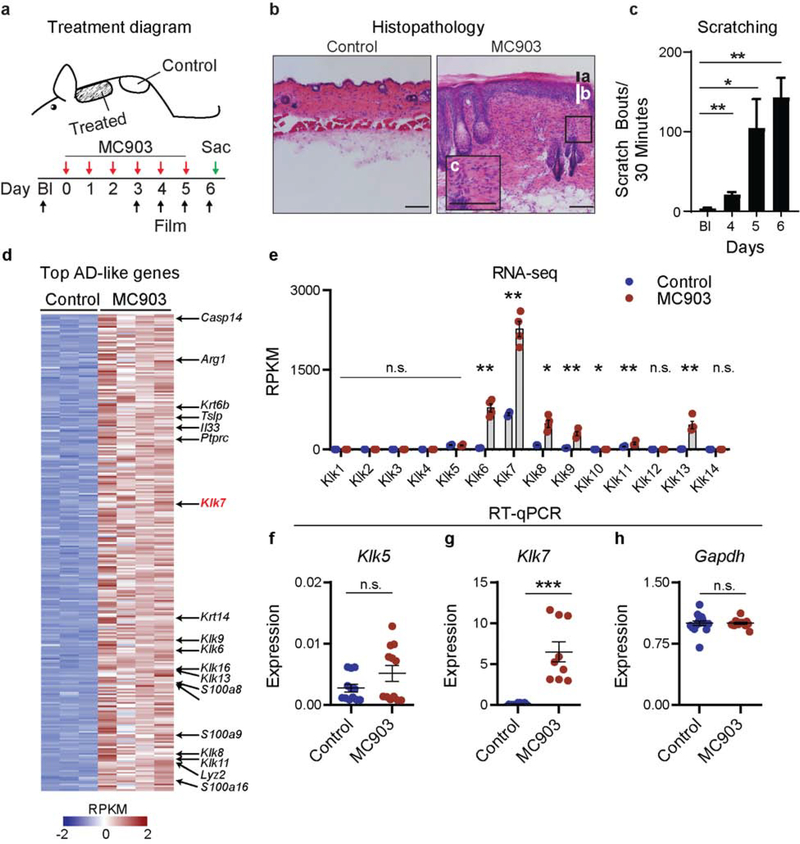
Figure 2. Klk7 is overexpressed in lesional murine AD-like skin.
a. Schematic of murine AD model. Control skin tissues were taken from non-lesional skin caudal to the treated area. b. Representative H&E section of control and lesional mouse skin after six MC903 treatments. Note presence of hyperkeratosis (a), acanthosis (b), and mixed lymphocyte infiltration (c) that define human AD lesions. n = 3 biological pairs. c. Mice develop severe spontaneous scratching behavior directed at the treated site after MC903 treatment. Statistical comparisons are made against baseline scratching. n=6 mice. d-e. RNA-seq of mouse control (ethanol vehicle) and MC903 treated skin, n = 3–4 mice per group. d. Heat map showing z-scored RPKMs of genes differentially expressed by ≥2-fold, adjusted p<0.05, and base mean expression values ≥1000. e. RPKM values of all Klks expressed in skin samples of control- and MC903-treated mice. f-h. RT-qPCR of f. Klk5 and g. Klk7 expression in mouse control- and MC903-treated skin normalized to h. Gapdh. n = 3 biological pairs. Error bars represent SEM. n.s. no significance. * p<0.05. ** p<0.01. *** p<0.001. The scale bars represent 200 μm.