Table 1.
Bisphenols ranked according to the mean relative peak Ca2+ signal induced at 10 μM, i.e., the peak Ca2+ signal induced by the bisphenol at 10 μM divided by the peak Ca2+ signal induced by progesterone at 5 μM in the same experiment.
| Rank | Name | CAS number | Abbrevation | Mean relative peak Ca2+ signal at 10 μM (in %) (n = 3) | Chemical structure | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive hits | 1 | Bisphenol G | 127-54-8 | BPG | 109.02 |  |
| 2 | Bisphenol AF | 1478-61-1 | BPAF | 57.95 |  |
|
| 3 | Bisphenol C | 79-97-0 | BPC | 21.67 |  |
|
| 4 | Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether | 1675-54-3 | BADGE | 14.79 |  |
|
| 5 | Bisphenol B | 77-40-7 | BPB | 11.75 |  |
|
| 6 | Bisphenol BP | 1844-01-5 | BPBP | 9.09 |  |
|
| Negative hits | 7 | Bisphenol E | 2081-08-5 | BPE | 5.37 |  |
| 8 | Bisphenol F | 620-92-8 | BPF | 5.09 |  |
|
| 9 | Bisphenol S | 80-09-1 | BPS | 4.41 |  |
|
| 10 | Bisphenol A | 80-05-7 | BPA | 1.44 | 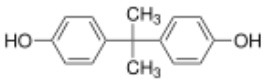 |
|
Based on their ability to induce Ca2+ signals, the bisphenols are categorized into “positive hits,” which induced mean relative peak Ca2+ signals above that of the negative controls (HTF+ with vehicle) ± 3 × SD (0.0 ± 3 × 2.3 = 6.9%) and “negative hits.” CAS number, abbreviation, and chemical structure are also listed in the table.
