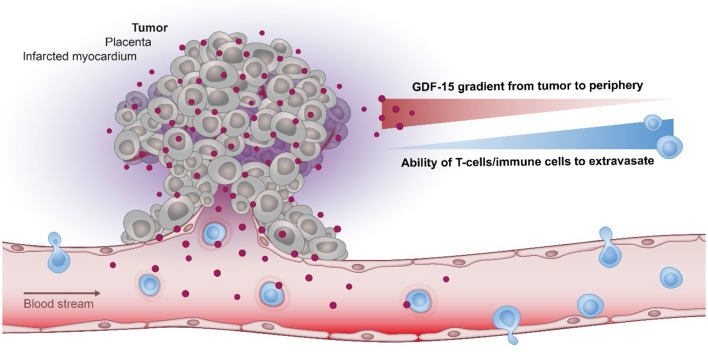
Figure 2.
The role of GDF-15 in immune modulation. In various pathological conditions, GDF-15 correlates inversely with the ability of T cell to infiltrate the tumor, placenta, or the infarcted myocardium. As the most prominent physiological expression of GDF-15 is found in the placenta it may have evolved to protect the (semi-allogeneic) fetus by establishing a protective barrier at the placenta-fetal junction, thus shielding the fetus against maternal T cells.