Figure 8.
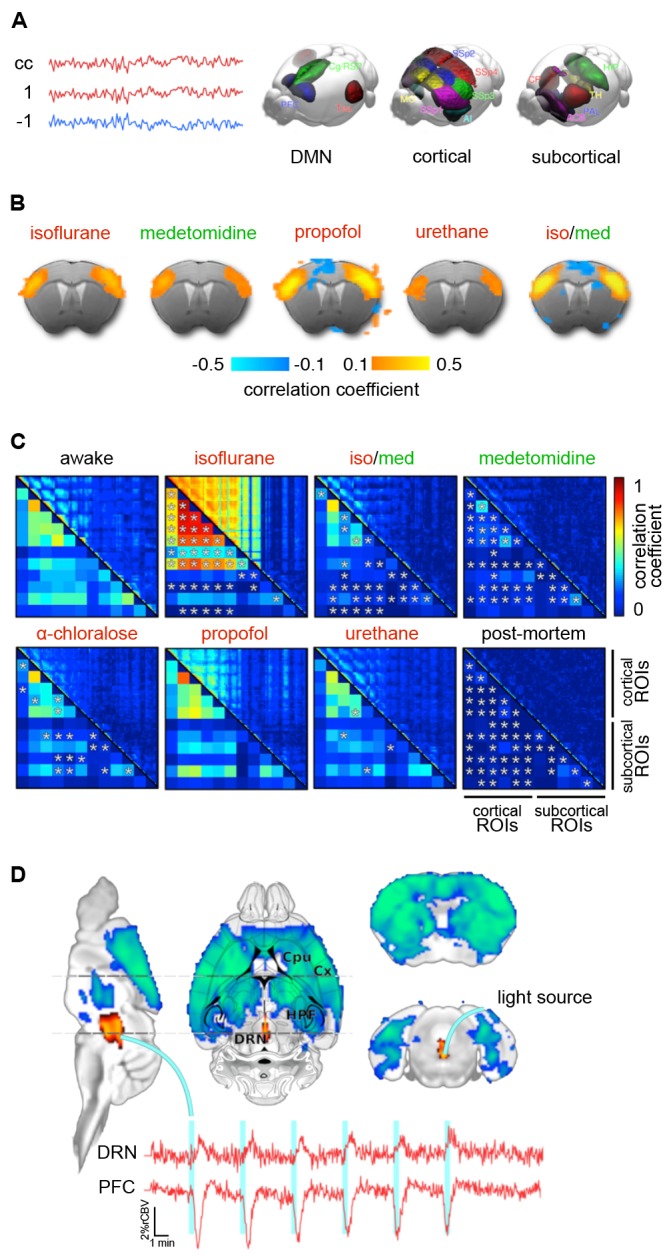
Functional connectivity (FC) in the mouse brain. (A) FC is defined by the correlation coefficient (cc) of remote brain areas. The left panel shows an assembly of important areas in murine FC, including the default mode network (DMN), cortical sensory-motor networks, and subcortical networks. (B) Murine FC correlation maps for five anesthetic protocols. Seed voxels in the anterior primary somatosensory cortex show anticorrelated time courses in the cingulate cortex. Anticorrelation is an essential criterion for anesthetic states in fMRI in which the FC is not restricted to its structural scaffold. (C) Correlation matrices in the rat for six different anesthetic protocols referenced against awake rats. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared with the awake group (t-test, p < 0.05, false discovery rate corrected). (D) Optogenetic stimulation of the dorsal raphé nuclei that send serotinergic projections into large parts of the brain leading to wide patterns of negative BOLD effects. Adapted from (A) Grandjean et al. (2019a); (B) based on Grandjean et al. (2014), reproducible using original data from the open repository, https://central.xnat.org; (C) adapted with permission from Paasonen et al. (2018), (D) Grandjean et al. (2019b).
