FIGURE 1.
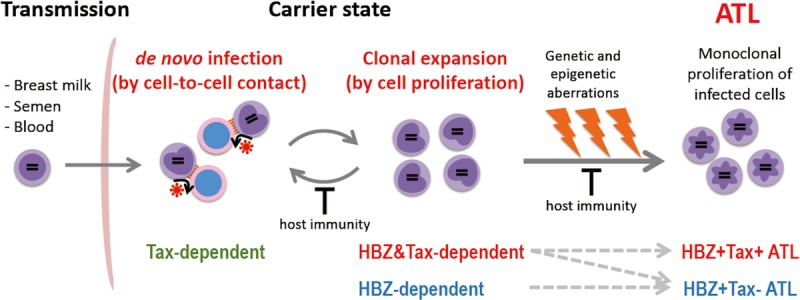
Propagation of HTLV-1-infected cells in vivo. HTLV-1 is transmitted by infected cells in breast milk, semen, and blood, and establishes infection by cell-to-cell contact. HTLV-1 spreads in vivo by de novo infection and clonal expansion. Tax is required for de novo infection since Tax drives viral replication. HBZ is critical for clonal expansion. Host immunity controls the number of infected cells and their clonality. In the carrier state, infected cells survive for a long period; genetic/epigenetic aberrations accumulate, and a malignant clone may emerge, resulting in ATL. Approximately half of ATL cases develop in a Tax-independent manner (i.e., Tax– ATL), while the other half retain the capacity to express Tax (Tax+ ATL).
