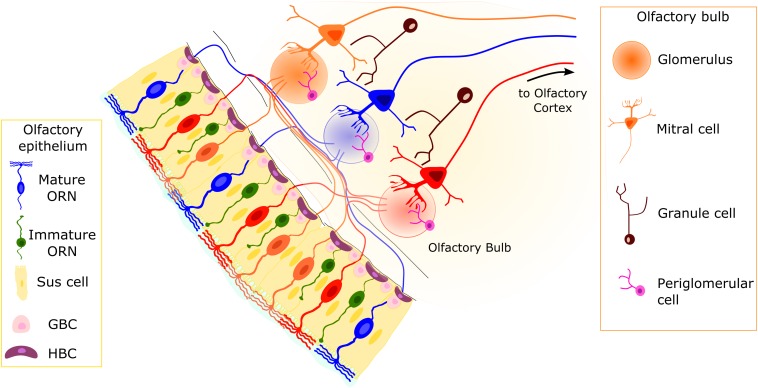
FIGURE 1.
Organization of the olfactory system. The pseudostratified olfactory epithelium (OE) consists of sustentacular (Sus) cells, olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs), and basal cells. The Sus cells have a columnar cell body, with an apical membrane with microvilli. Two main populations of neurons are present: mature and immature ORNs. Both ORN types are bipolar neurons with dendritic processes projecting toward the apical surface of the epithelium. In mature ORNs, several cilia protrude from the dendritic knob. Horizontal basal cells (HBCs) and globose basal cells (GBCs) constitute the stem cells of the OE. They are able to replace the different cell types on a daily basis or in case of injury. Axons from ORNs expressing the same odorant receptor type (represented by ORNs of the same color) converge in the olfactory bulb (OB) in round structures dense with synapses, called glomeruli. The second-order neurons (mitral/tufted cells) have a single dendrite projecting to a single glomerulus and lateral dendrites that contact dendrites of granule cells.