Figure 7.
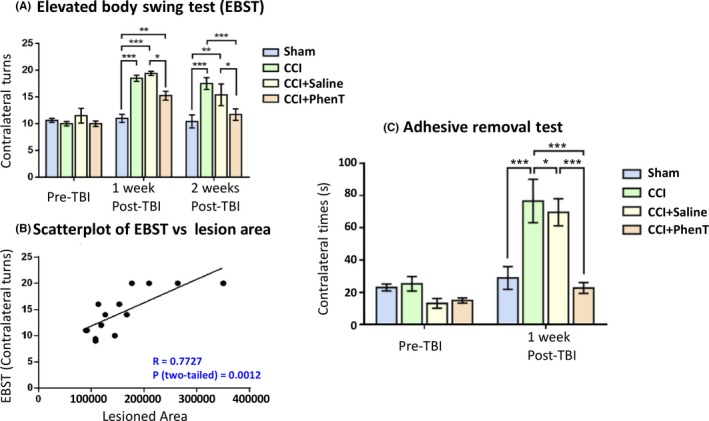
PhenT mitigates modTBI‐induced impairments in Elevated Body Swing Test (EBST) (impairments in which associate with greater TBI‐induced lesion size) as well as in Adhesive removal test (a measure of sensory/motor neglect). PhenT treatment (2.5 mg/kg, BID × 5 days post‐CCI) improved motor asymmetry, as revealed by behavioral measurement and correlation between behavioral evaluation and lesion size.41 A, Motor asymmetry measured by EBST. Analysis by two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni t‐test. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 4/group (SHAM, CCI, CCI + Saline), n = 7 (CCI + PhenT). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, compared among each group. B, Correlation between EBST and contusion lesion area was significant within Sham, CCI, CCI + Saline, CCI + PhenT groups at 2 wk after CCI. Analysis by Pearson's Correlation. n = 14, r = .7727, P (two‐tailed) = .0012. (C) Adhesive removal test: PhenT ameliorated sensory/motor neglect induced by CCI.41 CCI produces altered sensor/motor function, shown by spending more time to remove a sticker from the contralateral forepaw evaluated 1 wk after TBI in comparison to pre‐TBI (PRE). PhenT treatment (2.5 mg/kg BID × 5 days post‐CCI) significantly reduce this deficit. Analysis by two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni t‐test. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 4 (Sham, CCI, CCI + Saline), n = 7 (CCI + PhenT). *P < .05, ***P < .001, compared among each group
