Figure 2.
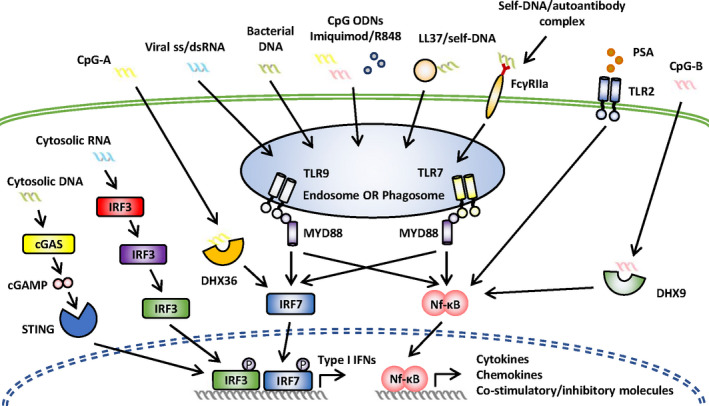
Routes of pDC sensing. Endosomal pathways: TLR7 senses RNA viruses and endogenous RNA, whereas TLR9 detects prokaryotes containing unmethylated CpG‐rich DNA sequences and endogenous DNA. Both TLR7 and TLR9 sense synthetic TLR ligands (CpG ODNs/imiquimod/R848) and immune complexes (self‐DNA/autoantibody and LL37/self‐DNA complexes mediated by FcγIIa). Non‐endosomal pathways: The cGAS (cyclic GMP‐AMP (cGAMP) synthase)–STING (stimulator of interferon genes) pathway senses cytosolic DNA and triggers an IRF3‐mediated IFN‐I production. Retinoic acid‐inducible gene I (RIG‐I) senses replicate viral RNA, recruits the mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein adaptor protein and leads to IFN‐I production. (DExD/H)‐box helicases DHX36 and DHX9 sense CpG ODNs, with the former selectively binding to CpG‐A and activating the IRF7 pathway and the latter selectively binding CpG‐B and activating the Nf‐ĸB pathway. pDCs sense polysaccharide A (PSA) via cytosolic TLR2 and activate the Nf‐ĸB pathway.
