Table 1.
Nutritional agonists of PPAR-γ. The table summarizes the main nutrients activator of PPAR-γ and their chemical structures.
| PPAR-γ Agonists | Structure | Food |
|---|---|---|
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) |
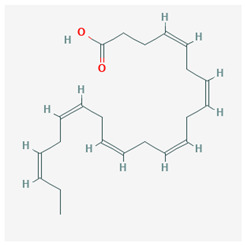 CID = 445,580 |
Sea food and fish oil |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) |
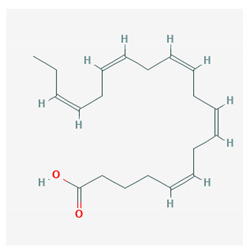 CID = 446,284 |
Sea food and fish oil |
| Curcumin |
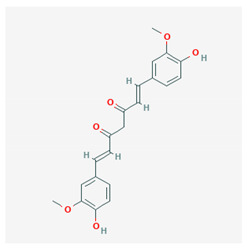 CID = 969,516 |
Turmeric |
| Carvacrol |
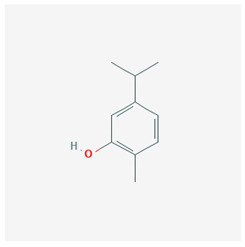 CID = 10,364 |
Thyme and oregano |
| Capsaicin |
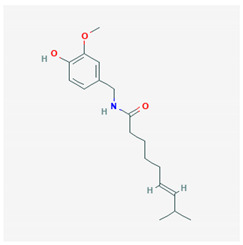 CID = 1,548,943 |
Hot pepper |
| Carnosic acid |
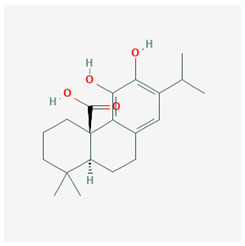 CID = 65,126 |
Rosemary and sage |
| Carnosol |
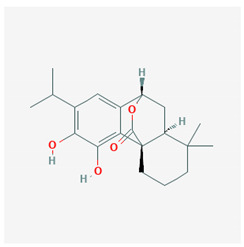 CID = 442,009 |
Rosemary and sage |
| Punicic acid |
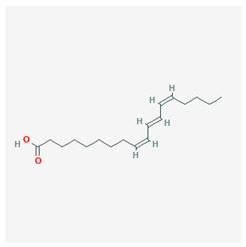 CID = 5,281,126 |
Pomegranate seed oil |
| Citral |
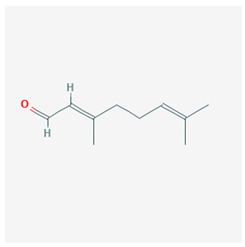 Geranial CID = 638,011 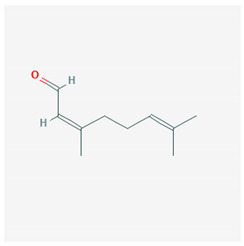 Neral CID = 643,779 |
Lemongrass |
