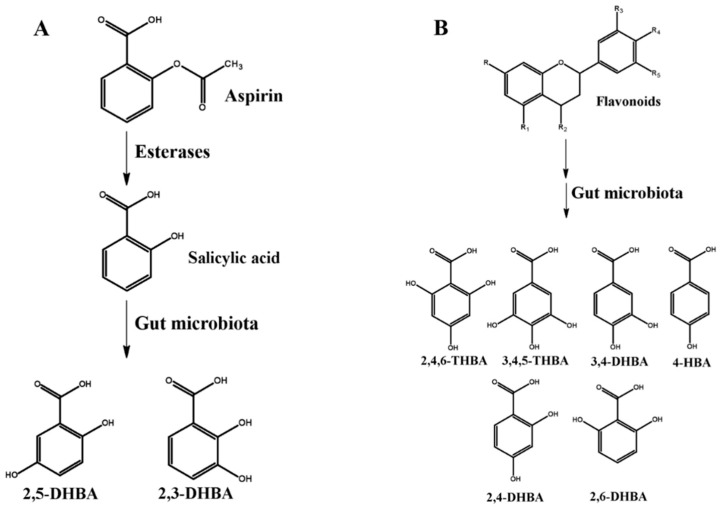
Figure 2.
Metabolism of aspirin and flavonoids to generate hydroxybenzoic acids. (A) Aspirin metabolism generates 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid (2,3-DHBA) and 2,5-DHBA through CYP450 reactions in the liver [61]. DHBAs have also been shown to be generated through microbial metabolism of aspirin/salicylic acid [12]. (B) Flavonoid metabolism generates metabolites 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoic acid (2,4,6-THBA), 3,4-DHBA, 3,4,5-THBA, 4-HBA, 2,4-DHBA, 2,6-DHBA through microbial degradation in the intestine [11,45,56,58]. R-R5 represent various functional groups (example -hydroxy, -ketone, -hydrogen, -methoxy, etc.) that are appended/attached to the flavonoid backbone to generate different groups of flavonoids.