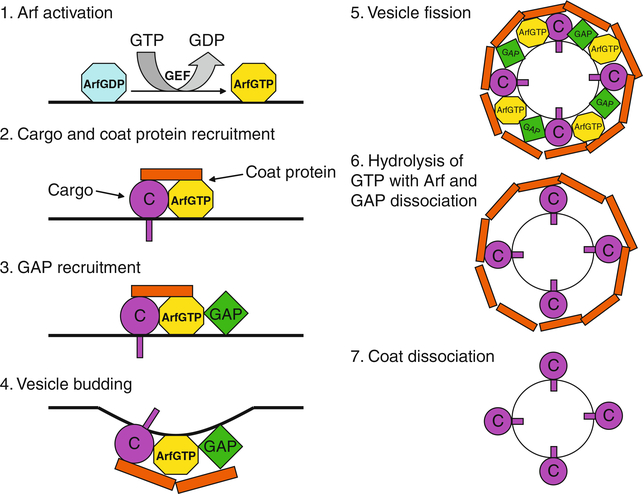
Fig. 2.
Model for Arf1 function in membrane traffic. Arf is activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that catalyzes GTP exchange for GDP at the membrane. Next, the activated Arf·GTP recruits coat protein. The coat protein·Arf·GTP complex traps cargo (C). GTPase-activating protein (GAP) is then recruited to membrane sites through binding to the coat protein·Arf·GTP complex, triggering membrane deformation and subsequent vesicle formation. Fission releases the newly formed coated vesicle from the membrane. After vesicle budding, GAP hydrolyzes GTP on Arf, leading to the inactivation of Arf and subsequent dissociation of Arf and GAP from the cargo-containing vesicle. Coat proteins eventually dissociate from the vesicle surface, allowing the vesicle to dock and fuse with acceptor membranes.