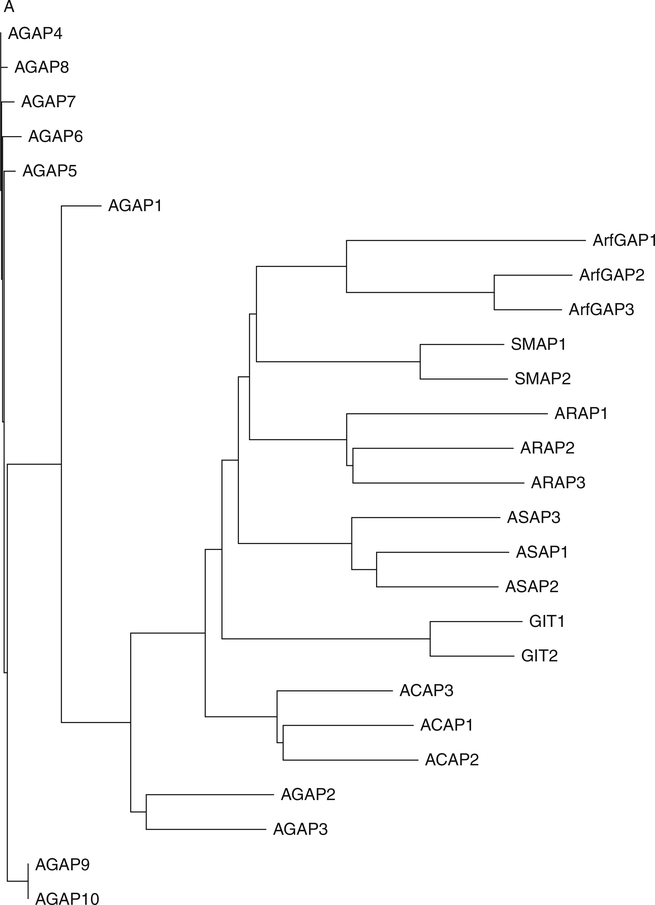
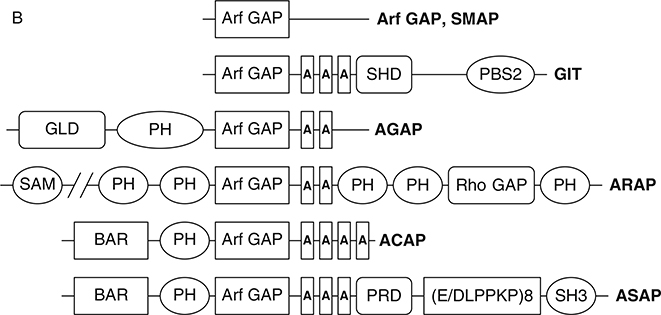
Fig. 3.
Arf GAP family. (A) Arf GAP family phylogram. The phylogram, edited using Tree-View, was obtained from the multiple sequence alignment of Arf GAP domains using ClustalW2. The branch lengths in the phylogram are proportional to the estimated divergence along each branch. Accession #s for human Arf GAPs: Arf GAP1 = NM_018209; Arf GAP2 = NM_032389; Arf GAP3 = NM_014570; Git1 = NM_014030; Git2 = NM_057169; ASAP1 = NM_018482; ASAP2 = NM_003887; ASAP3 = NM_017707; ACAP1 = NM_014716; ACAP2 = NM_012287; ACAP3 = NM_030649; AGAP1 = NM_014914; AGAP2 = NM_014770; AGAP3 = NM_031946; AGAP4 = NM_133446; AGAP5 = XM_001132588; AGAP6 = NM_001077665; AGAP7 = NM_001077685; AGAP8 = NM_001077686; AGAP9 = XM_001716810; AGAP10 = XM_001714786; ARAP1 = NM_015242; ARAP2 = NM_015230; ARAP3 = NM_022481; SMAP1 = AY055004; SMAP2 = NM_022733. (B) Schematic of human Arf GAPs. All Arf GAPs have a conserved Arf GAP domain. The other domains are as follows: Ank, ankyrin repeats; BAR, Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs; PBS, paxillin-binding site; PH, pleckstrin homology; SAM, sterile alpha motif; SH3, Src-homology 3; SHD, Spa2 homology domain; PRD, proline rich; GLD, GTP-binding domain.